Ectopic expression of hepatitis C virus core protein differentially regulates nuclear transcription factors
- PMID: 9811706
- PMCID: PMC110482
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.12.9722-9728.1998
Ectopic expression of hepatitis C virus core protein differentially regulates nuclear transcription factors
Abstract
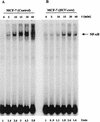
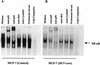
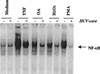
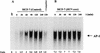
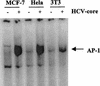
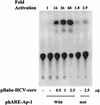
The putative core protein of hepatitis C virus (HCV) regulates cellular growth and a number of cellular promoters. To further understand its effect, we investigated the role of the core protein in the endogenous regulation of two distinct transcription factors, nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) and activating protein-1 (AP-1), and the related mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MAPKK) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). Stable cell transfectants expressing the HCV core protein suppressed tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-induced NF-kappaB activation. Supershift analysis revealed that NF-kappaB consists of p50 and p65 subunits. This correlated with inhibition of the degradation of IkappaBalpha, the inhibitory subunit of NF-kappaB. The effect was not specific to TNF, as suppression in core protein-expressing cells was also observed in response to a number of other inflammatory agents known to activate NF-kappaB. In contrast to the effect on NF-kappaB, the HCV core protein constitutively activated AP-1, which correlated with the activation of JNK and MAPKK, which are known to regulate AP-1. These observations indicated that the core protein targets transcription factors known to be involved in the regulation of inflammatory responses and the immune system.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Suppression of tumor necrosis factor-activated nuclear transcription factor-kappaB, activator protein-1, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and apoptosis by beta-lapachone.Biochem Pharmacol. 1999 Apr 1;57(7):763-74. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(98)00354-2. Biochem Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10075082
-
Resveratrol suppresses TNF-induced activation of nuclear transcription factors NF-kappa B, activator protein-1, and apoptosis: potential role of reactive oxygen intermediates and lipid peroxidation.J Immunol. 2000 Jun 15;164(12):6509-19. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.12.6509. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10843709
-
IL-13 suppresses TNF-induced activation of nuclear factor-kappa B, activation protein-1, and apoptosis.J Immunol. 1998 Sep 15;161(6):2863-72. J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9743347
-
Hepatitis C virus core protein enhances NF-kappaB signal pathway triggering by lymphotoxin-beta receptor ligand and tumor necrosis factor alpha.J Virol. 1999 Feb;73(2):1672-81. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.2.1672-1681.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 9882379 Free PMC article.
-
Vesnarinone suppresses TNF-induced activation of NF-kappa B, c-Jun kinase, and apoptosis.J Immunol. 2000 Jun 1;164(11):5815-25. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.11.5815. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10820260
Cited by
-
Responses of nontransformed human hepatocytes to conditional expression of full-length hepatitis C virus open reading frame.Am J Pathol. 2007 Dec;171(6):1831-46. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.070413. Epub 2007 Nov 8. Am J Pathol. 2007. PMID: 17991716 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-initiating stem-like cells and drug resistance: carcinogenesis through Toll-like receptors, environmental factors, and virus.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2013 Apr;3(2):152-64. doi: 10.1007/s13346-012-0115-x. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2013. PMID: 25787983 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis C virus and its roles in cell proliferation.J Gastroenterol. 2002;37 Suppl 13:50-4. doi: 10.1007/BF02990100. J Gastroenterol. 2002. PMID: 12109666
-
Effect of hepatitis C virus core protein on the molecular profiling of human B lymphocytes.Mol Med. 2006 Jan-Mar;12(1-3):47-53. doi: 10.2119/2006-00020.Wu. Mol Med. 2006. PMID: 16838065 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis C virus core protein upregulates serine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1 and impairs the downstream akt/protein kinase B signaling pathway for insulin resistance.J Virol. 2008 Mar;82(6):2606-12. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01672-07. Epub 2007 Dec 26. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18160431 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baeuerle P A, Baltimore D. NF-κB: ten years after. Cell. 1996;87:13–20. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin A S. The NF-κB and IκB proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:649–681. - PubMed
-
- Beidler D R, Tewari M, Friesen M, Poirier G, Dixit V M. The baculovirus p35 protein inhibits Fas- and tumor necrosis factor-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:16526–16528. - PubMed
-
- Bertin J, Armstrong R C, Ottilie S, Martin D A, Wang Y, Banks S, Wang G H, Senkevich T G, Alnemri E S, Moss B, Lenardo M J, Tomaselli K J, Cohen J I. Death effector domain-containing herpesvirus and poxvirus proteins inhibit both Fas- and TNFR1-induced apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:1172–1176. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

