Neutralizing antibodies from the sera of human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected individuals bind to monomeric gp120 and oligomeric gp140
- PMID: 9811699
- PMCID: PMC110475
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.12.9656-9667.1998
Neutralizing antibodies from the sera of human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected individuals bind to monomeric gp120 and oligomeric gp140
Abstract
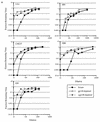
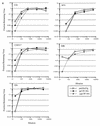
Antibodies that neutralize primary isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) appear during HIV-1 infection but are difficult to elicit by immunization with current vaccine products comprised of monomeric forms of HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein gp120. The limited neutralizing antibody response generated by gp120 vaccine products could be due to the absence or inaccessibility of the relevant epitopes. To determine whether neutralizing antibodies from HIV-1-infected patients bind to epitopes accessible on monomeric gp120 and/or oligomeric gp140 (ogp140), purified total immunoglobulin from the sera of two HIV-1-infected patients as well as pooled HIV immune globulin were selectively depleted of antibodies which bound to immobilized gp120 or ogp140. After passage of each immunoglobulin preparation through the respective columns, antibody titers against gp120 and ogp140 were specifically reduced at least 128-fold. The gp120- and gp140-depleted antibody fraction from each serum displayed reduced neutralization activity against three primary and two T-cell line-adapted (TCLA) HIV-1 isolates. Significant residual neutralizing activity, however, persisted in the depleted sera, indicating additional neutralizing antibody specificities. gp120- and ogp140-specific antibodies eluted from each column neutralized both primary and TCLA viruses. These data demonstrate the presence and accessibility of epitopes on both monomeric gp120 and ogp140 that are specific for antibodies that are capable of neutralizing primary isolates of HIV-1. Thus, the difficulties associated with eliciting neutralizing antibodies by using current monomeric gp120 subunit vaccines may be related less to improper protein structure and more to ineffective immunogen formulation and/or presentation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparison of HIV Type 1 ADA gp120 monomers versus gp140 trimers as immunogens for the induction of neutralizing antibodies.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2005 Jan;21(1):58-67. doi: 10.1089/aid.2005.21.58. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2005. PMID: 15665645
-
Characterization of antibody responses elicited by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 primary isolate trimeric and monomeric envelope glycoproteins in selected adjuvants.J Virol. 2006 Feb;80(3):1414-26. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.3.1414-1426.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16415019 Free PMC article.
-
Screening of HIV-1 Env glycoproteins for the ability to raise neutralizing antibody using DNA immunization and recombinant vaccinia virus boosting.Virology. 1997 Apr 14;230(2):265-74. doi: 10.1006/viro.1997.8478. Virology. 1997. PMID: 9143282
-
GP120: target for neutralizing HIV-1 antibodies.Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:739-69. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.24.021605.090557. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16551265 Review.
-
Aiming to induce broadly reactive neutralizing antibody responses with HIV-1 vaccine candidates.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2006 Jun;5(3):347-63. doi: 10.1586/14760584.5.3.347. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2006. PMID: 16827619 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Soluble CD4 broadens neutralization of V3-directed monoclonal antibodies and guinea pig vaccine sera against HIV-1 subtype B and C reference viruses.Virology. 2008 Oct 25;380(2):285-95. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2008.07.007. Epub 2008 Sep 18. Virology. 2008. PMID: 18804254 Free PMC article.
-
Purification and characterization of oligomeric envelope glycoprotein from a primary R5 subtype B human immunodeficiency virus.J Virol. 2002 Mar;76(6):2835-47. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.6.2835-2847.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11861851 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-subtype neutralizing antibodies induced in baboons by a subtype E gp120 immunogen based on an R5 primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope.J Virol. 1999 Jun;73(6):4640-50. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.6.4640-4650.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10233923 Free PMC article.
-
Use of a gp120 binding assay to dissect the requirements and kinetics of human immunodeficiency virus fusion events.J Virol. 1999 Dec;73(12):10346-58. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.12.10346-10358.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10559353 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 gp140 epitope recognition is influenced by immunoglobulin DH gene segment sequence.Immunogenetics. 2016 Feb;68(2):145-55. doi: 10.1007/s00251-015-0890-x. Epub 2015 Dec 19. Immunogenetics. 2016. PMID: 26687685 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Artenstein A W, VanCott T C, Sitz K V, Robb M L, Wagner K F, Veit S C D, Rogers A B, Garner R P, Byron J W, Burnett P R, Birx D L. Mucosal immune responses in four distinct compartments of women infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1: a comparison by site and correlation with clinical information. J Infect Dis. 1997;175:265–271. - PubMed
-
- Belshe R B, Graham B S, Keefer M C, Gorse G J, Wright P, Dolin R, Matthews T, Weinhold K, Bolognesi D P, Sposto R, Stablein D M, Twadell T, Berman P W, Gregory T, Izu A E, Walker M C, Fast P. Neutralizing antibodies to HIV-1 in seronegative volunteers immunized with recombinant gp120 from the MN strain of HIV-1. NIAID AIDS Vaccine Clinical Trials Network. JAMA. 1994;272:475–480. - PubMed
-
- Berman P W, Gregory T J, Riddle L, Nakamura G R, Champe M A, Porter J P, Wurm F M, Hershberg R D, Cobb E K, Eichberg J W. Protection of chimpanzees from infection by HIV-1 after vaccination with recombinant glycoprotein gp120 but not gp160. Nature. 1990;345:622–625. - PubMed
-
- Briant L, Benkirane M, Girard M, Hirn M, Iosef C, Devaux C. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 production in infected peripheral blood mononuclear cells by human leukocyte antigen class I-specific antibodies: evidence for a novel antiviral mechanism. J Virol. 1996;70:5213–5220. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

