Inhibition of NF-kappaB activation in combination with bcl-2 expression allows for persistence of first-generation adenovirus vectors in the mouse liver
- PMID: 9765474
- PMCID: PMC110346
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.11.9267-9277.1998
Inhibition of NF-kappaB activation in combination with bcl-2 expression allows for persistence of first-generation adenovirus vectors in the mouse liver
Abstract
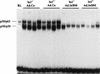
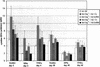
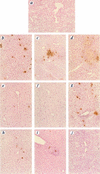
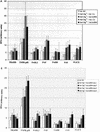
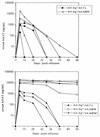
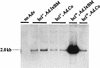
NF-kappaB is a key regulator of the innate antiviral immune response, due in part to its transcriptional activation of cytokines and adhesion molecules, which, in turn, function in chemotaxis and activation of inflammatory cells. We reported earlier that viral gene expression in hepatocytes transduced with first-generation (E1-deleted) adenoviruses induced NF-kappaB activation, elevation of serum cytokines, and hepatocellular apoptosis during the first days postinfusion. These events did not occur in mice infused with an adenovirus vector deleted for E1, E2, E3, and late gene expression. In the present study, we used an adenovirus expressing an IkappaBalpha supersuppressor (Ad.IkappaBM) and bcl-2 transgenic mice to unravel the role of virus-induced NF-kappaB activation and apoptosis in the clearance of recombinant adenovirus vectors from the liver. The combined action of IkappaBM and Bcl-2 allowed for vector persistence in livers of C57BL/6 x C3H mice. In the absence of Bcl-2, IkappaBM expression in mouse livers significantly reduced NF-kappaB activation, cytokine expression, leukocyte infiltration, and the humoral immune response against the transgene product; however, this was not sufficient to prevent the decline of vector DNA in transduced cells. Infusion of Ad.IkappaBM caused extended apoptosis predominantly in periportal liver regions, indicating that NF-kappaB activation may protect transduced hepatocytes from apoptosis induced by adenovirus gene products. To confer vector persistence, bcl-2 transgene expression was required to block virus-induced apoptosis if NF-kappaB protection was inactivated by IkappaBM. Expression of gene products involved in early stages of apoptotic pathways was up-regulated in response to virus infusion in bcl-2 transgenic mice, which may represent a compensatory effect. Our study supports the idea that the suppression of innate defense mechanisms improves vector persistence.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of Kupffer cell activation and viral gene expression in early liver toxicity after infusion of recombinant adenovirus vectors.J Virol. 1997 Nov;71(11):8798-807. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.11.8798-8807.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 9343240 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB promotes leaky expression of adenovirus genes in a replication-incompetent adenovirus vector.Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 27;6:19922. doi: 10.1038/srep19922. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26814140 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced toxicity, attenuated immunogenicity and efficient mediation of human p53 gene expression in vivo by an adenovirus vector with deleted E1-E3 and inactivated E4 by GAL4-TATA promoter replacement.Gene Ther. 1999 Mar;6(3):393-402. doi: 10.1038/sj.gt.3300825. Gene Ther. 1999. PMID: 10435089
-
NF-kappaB as a critical link between inflammation and cancer.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2009 Nov;1(5):a000141. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a000141. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2009. PMID: 20066113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innate immunity to adenovirus: lessons from mice.FEBS Lett. 2019 Dec;593(24):3461-3483. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13696. Epub 2019 Dec 8. FEBS Lett. 2019. PMID: 31769012 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Efficient gene transfer into human CD34(+) cells by a retargeted adenovirus vector.J Virol. 2000 Mar;74(6):2567-83. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.6.2567-2583.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10684271 Free PMC article.
-
An adenovirus-Epstein-Barr virus hybrid vector that stably transforms cultured cells with high efficiency.J Virol. 1999 Sep;73(9):7582-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.9.7582-7589.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10438848 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant adenovirus induces maturation of dendritic cells via an NF-kappaB-dependent pathway.J Virol. 2000 Oct;74(20):9617-28. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.20.9617-9628.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 11000234 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of biodistribution and safety of adenovirus vectors containing group B fibers after intravenous injection into baboons.Hum Gene Ther. 2005 Jun;16(6):664-77. doi: 10.1089/hum.2005.16.664. Hum Gene Ther. 2005. PMID: 15960598 Free PMC article.
-
B5-deficient vaccinia virus as a vaccine vector for the expression of a foreign antigen in vaccinia immune animals.Virology. 2007 May 10;361(2):356-63. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.11.020. Epub 2006 Dec 26. Virology. 2007. PMID: 17188733 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baeuerle P, Baltimore D. NF-κB: ten years after. Cell. 1996;87:13–20. - PubMed
-
- Barr D, Tubb J, Ferguson D, Scaria A, Lieber A, Wilson C, Perkins J, Kay M. Strain related variations in adenoviral mediated transgene expression from mouse hepatocytes in vivo: comparison between immunocompetent and immunodeficient inbred strains. Gene Ther. 1995;2:151–156. - PubMed
-
- Beg A A, Sha W C, Bronson R T, Ghosh S, Baltimore D. Embryonic lethality and liver degeneration in mice lacking the relA component of NF-κB. Nature. 1995;376:167–170. - PubMed
-
- Beg A A, Baltimore D. An essential role for NF-κB in preventing TNF-α-induced cell death. Science. 1996;274:782–784. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

