Coronavirus pseudoparticles formed with recombinant M and E proteins induce alpha interferon synthesis by leukocytes
- PMID: 9765403
- PMCID: PMC110275
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.11.8636-8643.1998
Coronavirus pseudoparticles formed with recombinant M and E proteins induce alpha interferon synthesis by leukocytes
Abstract
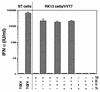
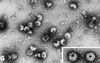
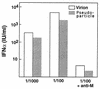
Transmissible gastroenteritis virus (TGEV), an enteric coronavirus of swine, is a potent inducer of alpha interferon (IFN-alpha) both in vivo and in vitro. Incubation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells with noninfectious viral material such as inactivated virions or fixed, infected cells leads to early and strong IFN-alpha synthesis. Previous studies have shown that antibodies against the virus membrane glycoprotein M blocked the IFN induction and that two viruses with a mutated protein exhibited a decreased interferogenic activity, thus arguing for a direct involvement of M protein in this phenomenon. In this study, the IFN-alpha-inducing activity of recombinant M protein expressed in the absence or presence of other TGEV structural proteins was examined. Fixed cells coexpressing M together with at least the minor structural protein E were found to induce IFN-alpha almost as efficiently as TGEV-infected cells. Pseudoparticles resembling authentic virions were released in the culture medium of cells coexpressing M and E proteins. The interferogenic activity of purified pseudoparticles was shown to be comparable to that of TGEV virions, thus establishing that neither ribonucleoprotein nor spikes are required for IFN induction. The replacement of the externally exposed, N-terminal domain of M with that of bovine coronavirus (BCV) led to the production of chimeric particles with no major change in interferogenicity, although the structures of the TGEV and BCV ectodomains markedly differ. Moreover, BCV pseudoparticles also exhibited interferogenic activity. Together these observations suggest that the ability of coronavirus particles to induce IFN-alpha is more likely to involve a specific, multimeric structure than a definite sequence motif.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interferon alpha inducing property of coronavirus particles and pseudoparticles.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1998;440:377-86. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-5331-1_49. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1998. PMID: 9782306
-
Single amino acid changes in the viral glycoprotein M affect induction of alpha interferon by the coronavirus transmissible gastroenteritis virus.J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):743-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.66.2.743-749.1992. J Virol. 1992. PMID: 1309909 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstituted coronavirus TGEV virosomes lose the virus ability to induce porcine interferon-alpha production.Vet Res. 1997;28(2):105-14. Vet Res. 1997. PMID: 9112732
-
Reconstituted coronavirus TGEV virosomes lose the virus ability to induce porcine interferon-alpha production.Vet Res. 1997;28(1):77-86. Vet Res. 1997. Corrected and republished in: Vet Res. 1997;28(2):105-14. PMID: 9172843 Corrected and republished.
-
An overview of immunological and genetic methods for detecting swine coronaviruses, transmissible gastroenteritis virus, and porcine respiratory coronavirus in tissues.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1997;412:37-46. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4899-1828-4_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1997. PMID: 9191988 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein-Protein Interactions of Viroporins in Coronaviruses and Paramyxoviruses: New Targets for Antivirals?Viruses. 2015 Jun 4;7(6):2858-83. doi: 10.3390/v7062750. Viruses. 2015. PMID: 26053927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subcellular localization of SARS-CoV structural proteins.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2006;581:297-300. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-33012-9_51. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2006. PMID: 17037547 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Transmissible Gastroenteritis Virus: An Update Review and Perspective.Viruses. 2023 Jan 27;15(2):359. doi: 10.3390/v15020359. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36851573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Porcine peripheral blood dendritic cells and natural interferon-producing cells.Immunology. 2003 Dec;110(4):440-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2003.01755.x. Immunology. 2003. PMID: 14632641 Free PMC article.
-
The PERK Arm of the Unfolded Protein Response Negatively Regulates Transmissible Gastroenteritis Virus Replication by Suppressing Protein Translation and Promoting Type I Interferon Production.J Virol. 2018 Jul 17;92(15):e00431-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00431-18. Print 2018 Aug 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29769338 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ankel H, Capobianchi M R, Castiletti C, Dianzani F. Interferon induction by HIV glycoprotein 120: role of the V3 loop. Virology. 1994;205:34–43. - PubMed
-
- Baudoux P. Ph. D. thesis. Paris-Grignon, France: Institut National Agronomique; 1996.
-
- Baudoux P, Charley B, Laude H. Recombinant expression of the TGEV membrane protein. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1995;380:305–310. - PubMed
-
- Baudoux, P., L. Besnardeau, C. Carrat, P. Rottier, B. Charley, and H. Laude. Interferon alpha inducing property of coronavirus particles and pseudoparticles. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol., in press. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

