A critical role of the p75 tumor necrosis factor receptor (p75TNF-R) in organ inflammation independent of TNF, lymphotoxin alpha, or the p55TNF-R
- PMID: 9763613
- PMCID: PMC2212501
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.188.7.1343
A critical role of the p75 tumor necrosis factor receptor (p75TNF-R) in organ inflammation independent of TNF, lymphotoxin alpha, or the p55TNF-R
Abstract
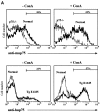
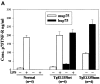
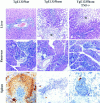
Despite overwhelming evidence that enhanced production of the p75 tumor necrosis factor receptor (p75TNF-R) accompanies development of specific human inflammatory pathologies such as multi-organ failure during sepsis, inflammatory liver disease, pancreatitis, respiratory distress syndrome, or AIDS, the function of this receptor remains poorly defined in vivo. We show here that at levels relevant to human disease, production of the human p75TNF-R in transgenic mice results in a severe inflammatory syndrome involving mainly the pancreas, liver, kidney, and lung, and characterized by constitutively increased NF-kappaB activity in the peripheral blood mononuclear cell compartment. This process is shown to evolve independently of the presence of TNF, lymphotoxin alpha, or the p55TNF-R, although coexpression of a human TNF transgene accelerated pathology. These results establish an independent role for enhanced p75TNF-R production in the pathogenesis of inflammatory disease and implicate the direct involvement of this receptor in a wide range of human inflammatory pathologies.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A murine transmembrane tumor necrosis factor (TNF) transgene induces arthritis by cooperative p55/p75 TNF receptor signaling.Eur J Immunol. 1997 Oct;27(10):2588-92. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830271018. Eur J Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9368614
-
A human tumor necrosis factor p75 receptor agonist stimulates in vitro T cell proliferation but does not produce inflammation or shock in the baboon.J Exp Med. 1996 Jul 1;184(1):165-71. doi: 10.1084/jem.184.1.165. J Exp Med. 1996. PMID: 8691130 Free PMC article.
-
Differential roles of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma in mouse hypermetabolic and anorectic responses induced by LPS.Eur Cytokine Netw. 2000 Dec;11(4):662-8. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2000. PMID: 11125311
-
Tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha): the good, the bad and potentially very effective.Immunol Cell Biol. 1996 Oct;74(5):434-43. doi: 10.1038/icb.1996.73. Immunol Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8912006 Review.
-
Peyer's patch organogenesis--cytokines rule, OK?Gut. 1997 Nov;41(5):707-9. doi: 10.1136/gut.41.5.707. Gut. 1997. PMID: 9414984 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Context-dependent induction of autoimmunity by TNF signaling deficiency.JCI Insight. 2022 Mar 8;7(5):e149094. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.149094. JCI Insight. 2022. PMID: 35104241 Free PMC article.
-
TNF Receptor 2 and Disease: Autoimmunity and Regenerative Medicine.Front Immunol. 2013 Dec 23;4:478. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00478. Front Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24391650 Free PMC article.
-
Selective blood-brain barrier permeabilization of brain metastases by a type 1 receptor-selective tumor necrosis factor mutein.Neuro Oncol. 2022 Jan 5;24(1):52-63. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noab177. Neuro Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34297105 Free PMC article.
-
Non-linear association between diabetes mellitus and pulmonary function: a population-based study.Respir Res. 2020 Nov 4;21(1):292. doi: 10.1186/s12931-020-01538-2. Respir Res. 2020. PMID: 33148273 Free PMC article.
-
A crucial role for tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 in synovial lining cells and the reticuloendothelial system in mediating experimental arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(2):R61. doi: 10.1186/ar2974. Epub 2010 Apr 6. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 20370892 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vassalli P. The pathophysiology of tumor necrosis factors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:411–452. - PubMed
-
- Vandenabeele P, Declercq W, Beyaert R, Fiers W. Two tumour necrosis factor receptors: structure and function. Trends Cell Biol. 1995;5:392–399. - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal BB, Natarajan K. Tumor necrosis factors: Developments during the last decade. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1996;7:93–124. - PubMed
-
- Seckinger P, Isaaz S, Dayer JM. Purification and biologic characterization of a specific tumor necrosis factor a inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:11966–11973. - PubMed
-
- Engelmann H, Novick D, Wallach D. Two tumor necrosis factor-binding proteins purified from human urine. Evidence for immunological cross-reactivity with cell surface tumor necrosis factor receptors. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:1531–1536. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

