Phosphoinositide-3-OH kinase-dependent regulation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 and protein kinase B/AKT by the integrin-linked kinase
- PMID: 9736715
- PMCID: PMC21621
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.19.11211
Phosphoinositide-3-OH kinase-dependent regulation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 and protein kinase B/AKT by the integrin-linked kinase
Abstract
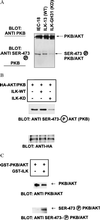
Integrin-linked kinase (ILK) is an ankyrin-repeat containing serine-threonine protein kinase capable of interacting with the cytoplasmic domains of integrin beta1, beta2, and beta3 subunits. Overexpression of ILK in epithelial cells disrupts cell-extracellular matrix as well as cell-cell interactions, suppresses suspension-induced apoptosis (also called Anoikis), and stimulates anchorage-independent cell cycle progression. In addition, ILK induces nuclear translocation of beta-catenin, where the latter associates with a T cell factor/lymphocyte enhancer-binding factor 1 (TCF/LEF-1) to form an activated transcription factor. We now demonstrate that ILK activity is rapidly, but transiently, stimulated upon attachment of cells to fibronectin, as well as by insulin, in a phosphoinositide-3-OH kinase [Pi(3)K]-dependent manner. Furthermore, phosphatidylinositol(3,4,5)trisphosphate specifically stimulates the activity of ILK in vitro, and in addition, membrane targetted constitutively active Pi(3)K activates ILK in vivo. We also demonstrate here that ILK is an upstream effector of the Pi(3)K-dependent regulation of both protein kinase B (PKB/AKT) and glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3). Specifically, ILK can directly phosphorylate GSK-3 in vitro and when stably, or transiently, overexpressed in cells can inhibit GSK-3 activity, whereas the overexpression of kinase-deficient ILK enhances GSK-3 activity. In addition, kinase-active ILK can phosphorylate PKB/AKT on serine-473, whereas kinase-deficient ILK severely inhibits endogenous phosphorylation of PKB/AKT on serine-473, demonstrating that ILK is involved in agonist stimulated, Pi(3)K-dependent, PKB/AKT activation. ILK is thus a receptor-proximal effector for the Pi(3)K-dependent, extracellular matrix and growth factor mediated, activation of PKB/AKT, and inhibition of GSK-3.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Cell-extracellular matrix interactions stimulate the AP-1 transcription factor in an integrin-linked kinase- and glycogen synthase kinase 3-dependent manner.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Nov;19(11):7420-7. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.11.7420. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10523630 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutive activation of protein kinase B and phosphorylation of p47phox by a membrane-targeted phosphoinositide 3-kinase.Curr Biol. 1996 Oct 1;6(10):1271-8. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)70713-6. Curr Biol. 1996. PMID: 8939574
-
The integrin-linked kinase regulates the cyclin D1 gene through glycogen synthase kinase 3beta and cAMP-responsive element-binding protein-dependent pathways.J Biol Chem. 2000 Oct 20;275(42):32649-57. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M000643200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10915780
-
Integrin-linked kinase (ILK): a "hot" therapeutic target.Biochem Pharmacol. 2000 Oct 15;60(8):1115-9. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(00)00444-5. Biochem Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 11007949 Review.
-
The role of integrin-linked kinase (ILK) in cancer progression.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003 Dec;22(4):375-84. doi: 10.1023/a:1023777013659. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003. PMID: 12884912 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrin-based adhesion compartmentalizes ALK3 of the BMPRII to control cell adhesion and migration.J Cell Biol. 2022 Dec 5;221(12):e202107110. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202107110. Epub 2022 Oct 7. J Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 36205720 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin-linked kinase regulates interphase and mitotic microtubule dynamics.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53702. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053702. Epub 2013 Jan 21. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23349730 Free PMC article.
-
How cardiomyocytes sense pathophysiological stresses for cardiac remodeling.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Mar;74(6):983-1000. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2373-0. Epub 2016 Oct 6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 27714411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The pseudoactive site of ILK is essential for its binding to alpha-Parvin and localization to focal adhesions.Mol Cell. 2009 Dec 11;36(5):819-30. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.11.028. Mol Cell. 2009. PMID: 20005845 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of integrin-linked kinase in the regulation of myogenic differentiation.J Cell Biol. 2000 Aug 21;150(4):861-72. doi: 10.1083/jcb.150.4.861. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10953009 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

