Coatomer, Arf1p, and nucleotide are required to bud coat protein complex I-coated vesicles from large synthetic liposomes
- PMID: 9736713
- PMCID: PMC21619
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.19.11199
Coatomer, Arf1p, and nucleotide are required to bud coat protein complex I-coated vesicles from large synthetic liposomes
Abstract
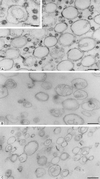
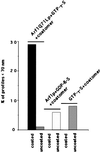
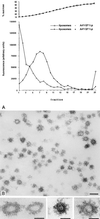
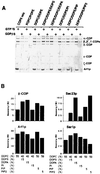
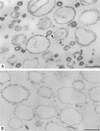
Synthetic coat protein complex I (COPI)-coated vesicles form spontaneously from large ( approximately 300 nm in diameter), chemically defined liposomes incubated with coatomer, Arf1p, and guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate. Coated vesicles are 40-70 nm in diameter, approximately the size of COPI vesicles formed from native membranes. The formation of COPI-coated buds and vesicles and the binding of Arf1p to donor liposomes depends on guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate. In contrast to the behavior of the COPII coat, coatomer binds to liposomes containing a variety of charged or neutral phospholipids. However, the formation of COPI buds and vesicles is stimulated by acidic phospholipids. In the absence of Arf1p, coatomer binds to liposomes containing dioleoylphosphatidic acid as a sole acidic phospholipid to form large coated surfaces without forming COPI-coated buds or vesicles. We conclude that Arf1p-GTP and coatomer comprise the minimum apparatus necessary to create a COPI-coated vesicle.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In vitro generation from the trans-Golgi network of coatomer-coated vesicles containing sialylated vesicular stomatitis virus-G protein.Methods. 2000 Apr;20(4):437-54. doi: 10.1006/meth.2000.0957. Methods. 2000. PMID: 10720465
-
COPI- and COPII-coated vesicles bud directly from the endoplasmic reticulum in yeast.Cell. 1995 Dec 29;83(7):1183-96. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90144-2. Cell. 1995. PMID: 8548805
-
Functional reconstitution of COPI coat assembly and disassembly using chemically defined components.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Jul 8;100(14):8253-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1432391100. Epub 2003 Jun 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12832619 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of formation of post Golgi vesicles from TGN membranes: Arf-dependent coat assembly and PKC-regulated vesicle scission.Biocell. 1996 Dec;20(3):287-300. Biocell. 1996. PMID: 9031596 Review.
-
Protein and lipid sorting between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi complex.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 1998 Oct;9(5):493-501. doi: 10.1006/scdb.1998.0256. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 1998. PMID: 9835636 Review.
Cited by
-
ArfGAP1 promotes COPI vesicle formation by facilitating coatomer polymerization.Cell Logist. 2011 Jul-Dec;1(4):139-154. doi: 10.4161/cl.1.4.18896. Epub 2011 Jul 1. Cell Logist. 2011. PMID: 22279613 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipase D: molecular and cell biology of a novel gene family.Biochem J. 2000 Feb 1;345 Pt 3(Pt 3):401-15. Biochem J. 2000. PMID: 10642495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Sar1 GTPase coordinates biosynthetic cargo selection with endoplasmic reticulum export site assembly.J Cell Biol. 2001 Jan 8;152(1):213-29. doi: 10.1083/jcb.152.1.213. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11149932 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate stimulates vesicle formation from liposomes by brain cytosol.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Mar 5;99(5):2842-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.261715599. Epub 2002 Feb 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 11867768 Free PMC article.
-
Prefission constriction of Golgi tubular carriers driven by local lipid metabolism: a theoretical model.Biophys J. 2003 Dec;85(6):3813-27. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(03)74796-1. Biophys J. 2003. PMID: 14645071 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Robinson M S. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994;6:538–644. - PubMed
-
- Bednarek S Y, Orci L, Schekman R. Trends Cell Biol. 1996;6:468–473. - PubMed
-
- Schekman R, Orci L. Science. 1996;271:1526–1533. - PubMed
-
- Bednarek S, Ravazzola M, Hosobuchi M, Amherdt M, Perrelet A, Schekman R, Orci L. Cell. 1995;83:1183–1196. - PubMed
-
- Orci L, Stamnes M, Ravazzola M, Amherdt M, Perrelet A, Söllner T H, Rothman J E. Cell. 1997;90:335–349. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

