Absence of effect of rufloxacin on theophylline pharmacokinetics in steady state
- PMID: 9736563
- PMCID: PMC105833
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.42.9.2359
Absence of effect of rufloxacin on theophylline pharmacokinetics in steady state
Abstract
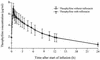
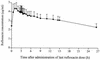
Several quinolone antibacterial agents are known to inhibit the metabolism of theophylline, with the potential to cause adverse events due to raised theophylline concentrations during coadministration. A randomized crossover study was therefore conducted with 12 healthy male volunteers (ages, 23 to 34 years; body weight, 64 to 101 kg) to evaluate a possible interaction between rufloxacin and theophylline. Both drugs were administered at steady state. Following the administration of an oral loading dose of 400 mg on day 1, rufloxacin was given orally at 200 mg once daily on days 2 to 7 during one period only. During both periods, 146 mg of theophylline was administered orally twice daily for 3 days (which were days 4 to 6 of the rufloxacin coadministration period) and intravenously once the next morning to test for an interaction. Theophylline and rufloxacin concentrations were measured by reversed-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography, the pharmacokinetics of theophylline at steady state following administration of the last dose were calculated by compartment-model-independent methods. To compare the treatments, analysis of variance-based point estimates and 90% confidence intervals (given in parentheses) were calculated for the mean ratios of the pharmacokinetic parameters from the test (rufloxacin coadministration) over those from the reference (theophylline without rufloxacin) period. These were as follows: maximum concentration at steady state, 1.01 (0.96 to 1.07); area under the concentration-time curve from 0 to 12 h, 0.98 (0.94 to 1.02); half-life, 0.99 (0.95 to 1.03); total clearance at steady state, 1. 02 (0.99 to 1.06); and volume of distribution in the elimination phase, 1.01 (0.97 to 1.05). In conclusion, rufloxacin did not affect theophylline pharmacokinetics at steady state. Therefore, therapeutic coadministration of rufloxacin and theophylline is not expected to cause an increased incidence of theophylline-related adverse events.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of single doses of rufloxacin on the disposition of theophylline and caffeine after single administration.Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol. 1991 Apr;29(4):133-8. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol. 1991. PMID: 2071262 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of temafloxacin on the pharmacokinetics of theophylline.Am J Med. 1991 Dec 30;91(6A):76S-80S. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(91)90315-o. Am J Med. 1991. PMID: 1662899
-
Effects of 2 quinolone antibacterials, temafloxacin and enoxacin, on theophylline pharmacokinetics.Clin Pharmacokinet. 1992;22 Suppl 1:65-74. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199200221-00012. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1992. PMID: 1319873 Clinical Trial.
-
[The effect of new quinolone antimicrobial agents and macrolide antibiotics on the clearance of theophylline].Nihon Rinsho. 1996 Nov;54(11):3125-9. Nihon Rinsho. 1996. PMID: 8950966 Review. Japanese.
-
Comparison of single preoperative oral rufloxacin versus perioperative ciprofloxacin as prophylactic agents in transurethral surgery.Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2000 Apr;72(1):15-20. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2000. PMID: 10875161 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacokinetic aspects of treating infections in the intensive care unit: focus on drug interactions.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2001;40(11):833-68. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200140110-00004. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2001. PMID: 11735605 Review.
-
Comparative pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the newer fluoroquinolone antibacterials.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2001;40(3):169-87. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200140030-00003. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2001. PMID: 11327197 Review.
References
-
- Benet L Z, Øie S, Schwartz J B. Design and optimization of dosage regimens; pharmacokinetic data. In: Hardman J G, Limbird L E, Molinoff P B, Ruddon R W, Gilman A G, editors. Goodman and Gilman’s the pharmacological basis of therapeutics. 9th ed. New York, N.Y: McGraw-Hill Book Co.; 1996. pp. 1707–1792.
-
- Boerema J B J, Bach D, Jol C, Pahlmann W. Penetration of rufloxacin into human prostatic tissue and fluid. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991;28:547–554. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

