E1B 55-kilodalton-associated protein: a cellular protein with RNA-binding activity implicated in nucleocytoplasmic transport of adenovirus and cellular mRNAs
- PMID: 9733834
- PMCID: PMC110131
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.10.7960-7971.1998
E1B 55-kilodalton-associated protein: a cellular protein with RNA-binding activity implicated in nucleocytoplasmic transport of adenovirus and cellular mRNAs
Abstract
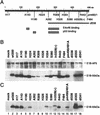
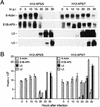
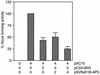
The adenovirus type 5 (Ad5) early 1B 55-kDa protein (E1B-55kDa) is a multifunctional phosphoprotein that regulates viral DNA replication and nucleocytoplasmic RNA transport in lytically infected cells. In addition, E1B-55kDa provides functions required for complete oncogenic transformation of rodent cells in cooperation with the E1A proteins. Using the far-Western technique, we have isolated human genes encoding E1B-55kDa-associated proteins (E1B-APs). The E1B-AP5 gene encodes a novel nuclear RNA-binding protein of the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnRNP) family that is highly related to hnRNP-U/SAF-A. Immunoprecipitation experiments indicate that two distinct segments in the 55-kDa polypeptide which partly overlap regions responsible for p53 binding are required for complex formation with E1B-AP5 in Ad-infected cells and that this protein interaction is modulated by the adenovirus E4orf6 protein. Expression of E1B-AP5 efficiently interferes with Ad5 E1A/E1B-mediated transformation of primary rat cells. Furthermore, stable expression of E1B-AP5 in Ad-infected cells overcomes the E1B-dependent inhibition of cytoplasmic host mRNA accumulation. These data suggest that E1B-AP5 might play a role in RNA transport and that this function is modulated by E1B-55kDa in Ad-infected cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structural analysis of the adenovirus type 5 E1B 55-kilodalton-E4orf6 protein complex.J Virol. 1997 Feb;71(2):1115-23. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.2.1115-1123.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 8995632 Free PMC article.
-
The E3 ubiquitin ligase activity associated with the adenoviral E1B-55K-E4orf6 complex does not require CRM1-dependent export.J Virol. 2011 Jul;85(14):7081-94. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02368-10. Epub 2011 May 11. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21561915 Free PMC article.
-
Export of adenoviral late mRNA from the nucleus requires the Nxf1/Tap export receptor.J Virol. 2011 Feb;85(4):1429-38. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02108-10. Epub 2010 Dec 1. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21123381 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-binding activity of the E1B 55-kilodalton protein from human adenovirus type 5.J Virol. 1998 Nov;72(11):9374-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.11.9374-9379.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9765492 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of synthesis, stability, phosphorylation, and interacting polypeptides of the 34-kilodalton product of open reading frame 6 of the early region 4 protein of human adenovirus type 5.J Virol. 1999 Feb;73(2):1245-53. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.2.1245-1253.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 9882328 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Relationship between SPRY and B30.2 protein domains. Evolution of a component of immune defence?Immunology. 2005 Dec;116(4):411-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2005.02248.x. Immunology. 2005. PMID: 16313355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct requirements of adenovirus E1b55K protein for degradation of cellular substrates.J Virol. 2008 Sep;82(18):9043-55. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00925-08. Epub 2008 Jul 9. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18614635 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between polyadenylate-binding protein 1 and Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus ORF57 in accumulation of polyadenylated nuclear RNA, a viral long noncoding RNA.J Virol. 2013 Jan;87(1):243-56. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01693-12. Epub 2012 Oct 17. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23077296 Free PMC article.
-
A role for E1B-AP5 in ATR signaling pathways during adenovirus infection.J Virol. 2008 Aug;82(15):7640-52. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00170-08. Epub 2008 May 14. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18480432 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of endogenous human Argonautes and their miRNA partners in RNA silencing.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Jun 10;105(23):7964-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0800334105. Epub 2008 Jun 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18524951 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bar-Sagi D, Rotin D, Batzer A, Mandiyan V, Schlessinger J. SH3 domains direct cellular localization of signaling molecules. Cell. 1993;74:83–91. - PubMed
-
- Beltz G A, Flint S J. Inhibition of HeLa cell protein synthesis during adenovirus infection. J Mol Biol. 1979;131:353–373. - PubMed
-
- Binger M H, Flint S J. Accumulation of early and intermediate mRNA species during subgroup C adenovirus productive infections. Virology. 1984;136:387–403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

