The cytoplasmic tail of rhodopsin acts as a novel apical sorting signal in polarized MDCK cells
- PMID: 9732285
- PMCID: PMC2149337
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.142.5.1245
The cytoplasmic tail of rhodopsin acts as a novel apical sorting signal in polarized MDCK cells
Abstract
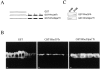
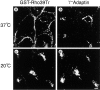
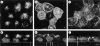
All basolateral sorting signals described to date reside in the cytoplasmic domain of proteins, whereas apical targeting motifs have been found to be lumenal. In this report, we demonstrate that wild-type rhodopsin is targeted to the apical plasma membrane via the TGN upon expression in polarized epithelial MDCK cells. Truncated rhodopsin with a deletion of 32 COOH-terminal residues shows a nonpolar steady-state distribution. Addition of the COOH-terminal 39 residues of rhodopsin redirects the basolateral membrane protein CD7 to the apical membrane. Fusion of rhodopsin's cytoplasmic tail to a cytosolic protein glutathione S-transferase (GST) also targets this fusion protein (GST-Rho39Tr) to the apical membrane. The targeting of GST-Rho39Tr requires both the terminal 39 amino acids and the palmitoylation membrane anchor signal provided by the rhodopsin sequence. The apical transport of GST-Rho39Tr can be reversibly blocked at the Golgi complex by low temperature and can be altered by brefeldin A treatment. This indicates that the membrane-associated GST-Rho39Tr protein may be sorted along a yet unidentified pathway that is similar to the secretory pathway in polarized MDCK cells. We conclude that the COOH-terminal tail of rhodopsin contains a novel cytoplasmic apical sorting determinant. This finding further indicates that cytoplasmic sorting machinery may exist in MDCK cells for some apically targeted proteins, analogous to that described for basolaterally targeted proteins.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sorting of rat liver and ileal sodium-dependent bile acid transporters in polarized epithelial cells.Am J Physiol. 1998 Nov;275(5):G1045-55. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1998.275.5.G1045. Am J Physiol. 1998. PMID: 9815035
-
Transport of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein to the cell surface is signal mediated in polarized and nonpolarized cells.J Cell Biol. 1996 May;133(3):543-58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.133.3.543. J Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8636230 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoplasmic signals mediate apical early endosomal targeting of endotubin in MDCK cells.Traffic. 2001 Jul;2(7):487-500. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0854.2001.20706.x. Traffic. 2001. PMID: 11422942
-
Cytoplasmic dynein regulation by subunit heterogeneity and its role in apical transport.J Cell Biol. 2001 Jun 25;153(7):1499-509. doi: 10.1083/jcb.153.7.1499. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11425878 Free PMC article.
-
Role of heterotrimeric G proteins in polarized membrane transport.J Cell Sci Suppl. 1993;17:27-32. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1993.supplement_17.5. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1993. PMID: 8144702 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of an outer segment targeting signal in the COOH terminus of rhodopsin using transgenic Xenopus laevis.J Cell Biol. 2000 Dec 25;151(7):1369-80. doi: 10.1083/jcb.151.7.1369. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11134067 Free PMC article.
-
Microfluidic approaches for epithelial cell layer culture and characterisation.Analyst. 2014 Jul 7;139(13):3206-18. doi: 10.1039/c4an00056k. Analyst. 2014. PMID: 24668405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Competing sorting signals guide endolyn along a novel route to lysosomes in MDCK cells.EMBO J. 2001 Nov 15;20(22):6256-64. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.22.6256. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11707397 Free PMC article.
-
SARA, a FYVE domain protein, affects Rab5-mediated endocytosis.J Cell Sci. 2002 Dec 15;115(Pt 24):4755-63. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00177. J Cell Sci. 2002. PMID: 12432064 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative splicing unmasks dendritic and axonal targeting signals in metabotropic glutamate receptor 1.J Neurosci. 2002 Mar 15;22(6):2196-205. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-06-02196.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 11896159 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adamus G, Arendt A, Zam ZS, McDowell JH, Hargrave PA. Use of peptides to select for anti-rhodopsin antibodies with desired amino acid sequence specificities. Pept Res. 1988;1:42–47. - PubMed
-
- Applebury ML, Hargrave PA. Molecular biology of the visual pigments. Vision Res. 1986;26:1881–1895. - PubMed
-
- Arreaza G, Brown AD. Sorting and intracellular trafficking of a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored protein and two hybrid transmembrane proteins with the same ectodomain in Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:23641–23647. - PubMed
-
- Balch WE, Glick BS, Rothman JE. Sequential intermediates in the pathway of intercompartmental transport in a cell-free system. Cell. 1984;39:525–536. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

