Functional gap junctions in the schwann cell myelin sheath
- PMID: 9722620
- PMCID: PMC2132877
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.142.4.1095
Functional gap junctions in the schwann cell myelin sheath
Abstract
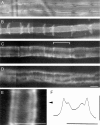
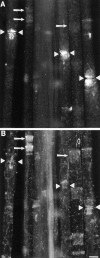
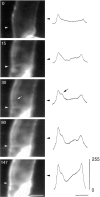
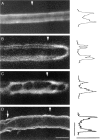
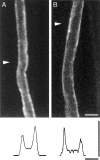
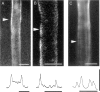
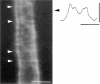
The Schwann cell myelin sheath is a multilamellar structure with distinct structural domains in which different proteins are localized. Intracellular dye injection and video microscopy were used to show that functional gap junctions are present within the myelin sheath that allow small molecules to diffuse between the adaxonal and perinuclear Schwann cell cytoplasm. Gap junctions are localized to periodic interruptions in the compact myelin called Schmidt-Lanterman incisures and to paranodes; these regions contain at least one gap junction protein, connexin32 (Cx32). The radial diffusion of low molecular weight dyes across the myelin sheath was not interrupted in myelinating Schwann cells from cx32-null mice, indicating that other connexins participate in forming gap junctions in these cells. Owing to the unique geometry of myelinating Schwann cells, a gap junction-mediated radial pathway may be essential for rapid diffusion between the adaxonal and perinuclear cytoplasm, since this radial pathway is approximately one million times faster than the circumferential pathway.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Connexin32-containing gap junctions in Schwann cells at the internodal zone of partial myelin compaction and in Schmidt-Lanterman incisures.J Neurosci. 2004 Mar 31;24(13):3186-98. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5146-03.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15056698 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenic expression of human connexin32 in myelinating Schwann cells prevents demyelination in connexin32-null mice.J Neurosci. 2005 Feb 9;25(6):1550-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3082-04.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15703409 Free PMC article.
-
Connexin channels in Schwann cells and the development of the X-linked form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease.Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2000 Apr;32(1):192-202. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0173(99)00081-8. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2000. PMID: 10751670 Review.
-
Prenylation-defective human connexin32 mutants are normally localized and function equivalently to wild-type connexin32 in myelinating Schwann cells.J Neurosci. 2005 Aug 3;25(31):7111-20. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1319-05.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16079393 Free PMC article.
-
Gap junction disorders of myelinating cells.Rev Neurosci. 2010;21(5):397-419. doi: 10.1515/revneuro.2010.21.5.397. Rev Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 21280457 Review.
Cited by
-
Episodic neurological dysfunction in hereditary peripheral neuropathy.Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2015 Jan-Mar;18(1):111-4. doi: 10.4103/0972-2327.144314. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2015. PMID: 25745327 Free PMC article.
-
The structural and functional integrity of peripheral nerves depends on the glial-derived signal desert hedgehog.J Neurosci. 2006 Jun 7;26(23):6364-76. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0157-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16763045 Free PMC article.
-
Pathomechanisms of mutant proteins in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease.Neuromolecular Med. 2006;8(1-2):217-42. doi: 10.1385/nmm:8:1-2:217. Neuromolecular Med. 2006. PMID: 16775378 Review.
-
Connexin29 is uniquely distributed within myelinating glial cells of the central and peripheral nervous systems.J Neurosci. 2002 Aug 1;22(15):6458-70. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-15-06458.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12151525 Free PMC article.
-
Connexin29 expression, immunocytochemistry and freeze-fracture replica immunogold labelling (FRIL) in sciatic nerve.Eur J Neurosci. 2002 Sep;16(5):795-806. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2002.02149.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12372015 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balice-Gordon, R.J. 1998. In vivo approaches to neuromuscular junction structure and function. In Methods in Cell Biology. C.P. Emerson and H.L. Sweeney, editors. Academic Press, San Diego, CA. 323–348. - PubMed
-
- Berg, H.C. 1983. Random Walks in Biology. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ. 142 pp.
-
- Bergoffen J, Scherer SS, Wang S, Oronzi-Scott M, Bone L, Paul DL, Chen K, Lensch MW, Chance P, Fischbeck K. Connexin mutations in X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Science. 1993;262:2039–2042. - PubMed
-
- Berthold, C.-H., and M. Rydmark. 1995. Morphology of normal peripheral axons. In The Axon. S.G. Waxman, J.D. Kocsis, and P.K. Stys, editors. Oxford University Press, New York. 13–48.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

