Epstein-Barr virus-transforming protein latent infection membrane protein 1 activates transcription factor NF-kappaB through a pathway that includes the NF-kappaB-inducing kinase and the IkappaB kinases IKKalpha and IKKbeta
- PMID: 9707608
- PMCID: PMC21469
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.17.10106
Epstein-Barr virus-transforming protein latent infection membrane protein 1 activates transcription factor NF-kappaB through a pathway that includes the NF-kappaB-inducing kinase and the IkappaB kinases IKKalpha and IKKbeta
Abstract
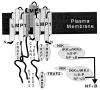
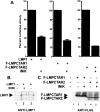
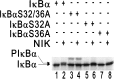
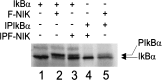
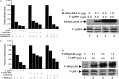
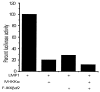
The Epstein-Barr virus oncoprotein latent infection membrane protein 1 (LMP1) is a constitutively aggregated pseudo-tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) that activates transcription factor NF-kappaB through two sites in its C-terminal cytoplasmic domain. One site is similar to activated TNFRII in associating with TNFR-associated factors TRAF1 and TRAF2, and the second site is similar to TNFRI in associating with the TNFRI death domain interacting protein TRADD. TNFRI has been recently shown to activate NF-kappaB through association with TRADD, RIP, and TRAF2; activation of the NF-kappaB-inducing kinase (NIK); activation of the IkappaB alpha kinases (IKKalpha and IKKbeta); and phosphorylation of IkappaB alpha. IkappaB alpha phosphorylation on Ser-32 and Ser-36 is followed by its degradation and NF-kappaB activation. In this report, we show that NF-kappaB activation by LMP1 or by each of its effector sites is mediated by a pathway that includes NIK, IKKalpha, and IKKbeta. Dominant negative mutants of NIK, IKKalpha, or IKKbeta substantially inhibited NF-kappaB activation by LMP1 or by each of its effector sites.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr virus latent infection membrane protein 1 TRAF-binding site induces NIK/IKK alpha-dependent noncanonical NF-kappaB activation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Jan 6;101(1):141-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2237183100. Epub 2003 Dec 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 14691250 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1 activates the JNK pathway through its extreme C terminus via a mechanism involving TRADD and TRAF2.J Virol. 1999 Feb;73(2):1023-35. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.2.1023-1035.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 9882303 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of TRAF2 and TRAF3 in Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1-induced alternative NF-kappaB activation.Virus Genes. 2010 Oct;41(2):174-80. doi: 10.1007/s11262-010-0505-4. Epub 2010 Jun 29. Virus Genes. 2010. PMID: 20585848
-
Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047224 Review.
-
LMP1 TRAFficking activates growth and survival pathways.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;597:173-87. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-70630-6_14. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17633026 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of TRAF6 on the biological behavior of human lung adenocarcinoma cell.Tumour Biol. 2013 Feb;34(1):231-9. doi: 10.1007/s13277-012-0543-8. Epub 2012 Oct 4. Tumour Biol. 2013. PMID: 23055197
-
Inhibition of TNFα-induced iNOS expression in HSV-tk transduced 9L glioblastoma cell lines by Marasmius oreades substances through NF-κB- and MAPK-dependent mechanisms.Mol Biol Rep. 2010 Dec;37(8):3801-12. doi: 10.1007/s11033-010-0035-0. Epub 2010 Mar 12. Mol Biol Rep. 2010. PMID: 20224909
-
Molecular pathways in virus-induced cytokine production.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2001 Mar;65(1):131-50. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.65.1.131-150.2001. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2001. PMID: 11238989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Possible interactions between the NS-1 protein and tumor necrosis factor alpha pathways in erythroid cell apoptosis induced by human parvovirus B19.J Virol. 1999 Oct;73(10):8762-70. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.10.8762-8770.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10482630 Free PMC article.
-
NF-kappaB activation by double-stranded-RNA-activated protein kinase (PKR) is mediated through NF-kappaB-inducing kinase and IkappaB kinase.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Feb;20(4):1278-90. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.4.1278-1290.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10648614 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

