ATP-mediated activation of RNA polymerase II transcription complexes
- PMID: 9699480
- PMCID: PMC6190198
ATP-mediated activation of RNA polymerase II transcription complexes
Abstract
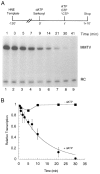
Transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II is a complex, multistep process that minimally involves transcription complex assembly, open complex formation, and promoter clearance. Hydrolysis of the beta--gamma phosphoanhydride bond of ATP has previously been shown to be required for open complex formation, as well as for the phosphorylation of the carboxy-terminal domain of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II. The observation that ATP-dependent activation of transcription complexes can be blocked by ATP analogues that contain nonhydrolyzable beta--gamma phosphoanhydride bonds (such as ATPgammaS) was exploited to develop a functional kinetic assay for ATP-activated transcription complexes. Activated complexes on the promoter present in the long terminal repeat of the proviral DNA of mouse mammary tumor virus were defined as those that could productively initiate transcription in the presence of excess ATPgammaS. Activation is dependent on treatment of assembled preinitiation complexes with ATP (or dATP) prior to addition of ATPgammaS. At least 15-35% of the total number of preinitiation complexes present become activated within 2 min in the presence of (d)ATP, and activation appears to be rapidly reversible. The time course of formation of activated complexes in the presence of dATP is characterized by two kinetic phases: a rapid formation followed by a relatively slow decay. Activated complexes were estimated to form with a half-time of less than 1 min.
Figures
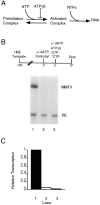
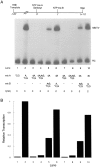
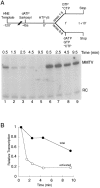
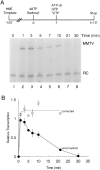
Similar articles
-
Promoter-dependent transcription by RNA polymerase II using immobilized enzyme complexes.J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3223-9. J Biol Chem. 1989. PMID: 2464595
-
ATP activates transcription initiation from promoters by RNA polymerase II in a reversible step prior to RNA synthesis.J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2962-8. J Biol Chem. 1988. PMID: 2449431
-
The RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex formed in the presence of ATP.Nucleic Acids Res. 1997 Oct 15;25(20):4079-84. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.20.4079. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997. PMID: 9321661 Free PMC article.
-
Promoter escape by RNA polymerase II.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 Sep 13;1577(2):208-223. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4781(02)00453-0. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002. PMID: 12213653 Review.
-
The role of activators in assembly of RNA polymerase II transcription complexes.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Apr;4(2):236-44. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80050-4. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994. PMID: 8032201 Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular ATP and Macropinocytosis: Their Interactive and Mutually Supportive Roles in Cell Growth, Drug Resistance, and EMT in Cancer.Subcell Biochem. 2022;98:61-83. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-94004-1_4. Subcell Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35378703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An energetic view of stress: Focus on mitochondria.Front Neuroendocrinol. 2018 Apr;49:72-85. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2018.01.001. Epub 2018 Jan 12. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2018. PMID: 29339091 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Buratowski S.; Hahn S.; Guarente L.; Sharp P. Five intermediate complexes in transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell 56:549–561; 1989. - PubMed
-
- Cai H.; Luse D. S. Transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in vitro. Properties of preinitiation, initiation, and elongation complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 262:298–304; 1987. - PubMed
-
- Conaway R. C.; Conaway J. W. ATP activates transcription initiation from promoters by RNA polymerase II in a reversible step prior to RNA synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 263:2962–2968; 1988. - PubMed
-
- Conaway R. C.; Conaway J. W. General initiation factors for RNA polymerase II. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 62:161–190; 1993. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
