The early region 4 orf4 protein of human adenovirus type 5 induces p53-independent cell death by apoptosis
- PMID: 9696808
- PMCID: PMC109936
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.9.7144-7153.1998
The early region 4 orf4 protein of human adenovirus type 5 induces p53-independent cell death by apoptosis
Abstract
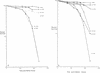
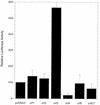
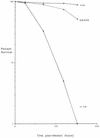
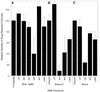
Previous studies by our group showed that infection of human and rodent cells by human adenovirus type 5 (Ad5) results in the induction of p53-independent apoptosis and cell death that are dependent upon transactivation of early region 4 (E4). To identify which E4 products are involved, studies were conducted with p53-deficient human SAOS-2 cells infected with various Ad5 E4 mutants. An E4orf6-deficient mutant was defective in cell killing, whereas another that expressed only E4orf6 and E4orf4 killed like wild-type virus, suggesting that E4orf6 may be responsible for cytotoxicity; however, a mutant expressing only E4orf4 induced high levels of cell death, indicating that this E4 product may also be able to induce cytotoxicity. To define the E4 cell death-inducing functions more precisely, cDNAs encoding individual E4 products were introduced into cells by DNA transfection in the absence of other Ad5 proteins. In cotransfections with a cDNA encoding firefly luciferase, enzymatic activity was high in all cases except with E4orf4, where luciferase levels were less than 20% of those in controls. In addition, drug selection of several cell types following transfection with retroviral vector DNA encoding individual E4 products as well as puromycin resistance yielded a large number of cell colonies except when E4orf4 was expressed. These data demonstrated that E4orf4 is the only E4 product capable of independent cell killing. Cell death induced by E4orf4 was due to apoptosis, as evidenced by 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) staining of cell nuclei in E4orf4-expressing cells. Thus, although E4orf6 may play some role, these results suggested that E4orf4 may be the major E4 product responsible for induction of p53-independent apoptosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by the adenovirus E4orf4 protein requires binding to the Balpha subunit of protein phosphatase 2A.J Virol. 2000 Sep;74(17):7869-77. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.17.7869-7877.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10933694 Free PMC article.
-
Adenovirus type 5 E4 open reading frame 4 protein induces apoptosis in transformed cells.J Virol. 1998 Apr;72(4):2975-82. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.4.2975-2982.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9525619 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of transformation and p53-dependent apoptosis by adenovirus type 5 E4orf6/7 cDNA.J Virol. 1999 Dec;73(12):10095-103. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.12.10095-10103.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10559324 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of apoptosis by adenovirus E4orf4 protein.Apoptosis. 2000 Jun;5(3):211-5. doi: 10.1023/a:1009644210581. Apoptosis. 2000. PMID: 11225841 Review.
-
The role of adenovirus E4orf4 protein in viral replication and cell killing.Oncogene. 2001 Nov 26;20(54):7855-65. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204862. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11753668 Review.
Cited by
-
R-Phycoerythrin Induces SGC-7901 Apoptosis by Arresting Cell Cycle at S Phase.Mar Drugs. 2016 Sep 12;14(9):166. doi: 10.3390/md14090166. Mar Drugs. 2016. PMID: 27626431 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by the adenovirus E4orf4 protein requires binding to the Balpha subunit of protein phosphatase 2A.J Virol. 2000 Sep;74(17):7869-77. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.17.7869-7877.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10933694 Free PMC article.
-
Caspase activation by adenovirus e4orf4 protein is cell line specific and Is mediated by the death receptor pathway.J Virol. 2001 Jan;75(2):789-98. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.2.789-798.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11134292 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis by live imaging of effects of the adenovirus E4orf4 protein on passage through mitosis of H1299 tumor cells.J Virol. 2015 Apr;89(8):4685-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03437-14. Epub 2015 Feb 4. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25653433 Free PMC article.
-
The Human Adenovirus Type 5 E4orf4 Protein Targets Two Phosphatase Regulators of the Hippo Signaling Pathway.J Virol. 2015 Sep;89(17):8855-70. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03710-14. Epub 2015 Jun 17. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26085163 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boyd J M, Malstrom S, Subramanian T, Venkatesh L K, Schaeper U, Elangovan B, D’Sa-Eipper C, Chinnadurai G. Adenovirus E1B 19 kDa and Bcl-2 proteins interact with a common set of cellular proteins. Cell. 1994;79:341–351. - PubMed
-
- Braithwaite A, Nelson C, Skulimowshi A, McGovern J, Pigott D, Jenkins J. Transactivation of the p53 oncogene by E1a gene products. Virology. 1990;177:595–605. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

