Bacterial SOS checkpoint protein SulA inhibits polymerization of purified FtsZ cell division protein
- PMID: 9683493
- PMCID: PMC107380
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.15.3946-3953.1998
Bacterial SOS checkpoint protein SulA inhibits polymerization of purified FtsZ cell division protein
Abstract
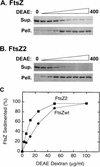
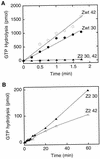
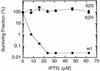
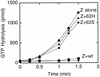
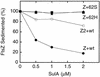
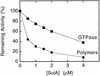
Cell division of Escherichia coli is inhibited when the SulA protein is induced in response to DNA damage as part of the SOS checkpoint control system. The SulA protein interacts with the tubulin-like FtsZ division protein. We investigated the effects of purified SulA upon FtsZ. SulA protein inhibits the polymerization and the GTPase activity of FtsZ, while point mutant SulA proteins show little effect on either of these FtsZ activities. SulA did not inhibit the polymerization of purified FtsZ2 mutant protein, which was originally isolated as insensitive to SulA. These studies define polymerization assays for FtsZ which respond to an authentic cellular regulator. The observations presented here support the notion that polymerization of FtsZ is central to its cellular role and that direct, reversible inhibition of FtsZ polymerization by SulA may account for division inhibition.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Inhibition of FtsZ polymerization by SulA, an inhibitor of septation in Escherichia coli.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Mar 17;95(6):2885-90. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.6.2885. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9501185 Free PMC article.
-
A cell division inhibitor SulA of Escherichia coli directly interacts with FtsZ through GTP hydrolysis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Apr 6;209(1):198-204. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.1489. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995. PMID: 7726836
-
SulA is able to block cell division in Escherichia coli by a mechanism different from sequestration.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 May 14;525(4):948-953. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.03.012. Epub 2020 Mar 12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 32173527
-
Regulation of Cell Division in Bacteria by Monitoring Genome Integrity and DNA Replication Status.J Bacteriol. 2020 Jan 2;202(2):e00408-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00408-19. Print 2020 Jan 2. J Bacteriol. 2020. PMID: 31548275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SosA in Staphylococci: an addition to the paradigm of membrane-localized, SOS-induced cell division inhibition in bacteria.Curr Genet. 2020 Jun;66(3):495-499. doi: 10.1007/s00294-019-01052-z. Epub 2020 Jan 10. Curr Genet. 2020. PMID: 31925496 Review.
Cited by
-
MadR1, a Mycobacterium tuberculosis cell cycle stress response protein that is a member of a widely conserved protein class of prokaryotic, eukaryotic and archeal origin.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2015 May;95(3):251-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2015.03.005. Epub 2015 Mar 13. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2015. PMID: 25829286 Free PMC article.
-
FtsZ collaborates with penicillin binding proteins to generate bacterial cell shape in Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 2004 Oct;186(20):6768-74. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.20.6768-6774.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15466028 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship among several key cell cycle events in the developmental cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120.J Bacteriol. 2006 Aug;188(16):5958-65. doi: 10.1128/JB.00524-06. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16885464 Free PMC article.
-
The SOS response regulates adaptive mutation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Jun 6;97(12):6646-51. doi: 10.1073/pnas.120161797. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10829077 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting of (D)MinC/MinD and (D)MinC/DicB complexes to septal rings in Escherichia coli suggests a multistep mechanism for MinC-mediated destruction of nascent FtsZ rings.J Bacteriol. 2002 Jun;184(11):2951-62. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.11.2951-2962.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 12003935 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bi E F, Lutkenhaus J. FtsZ ring structure associated with division in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1991;354:161–164. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

