The SNARE machinery is involved in apical plasma membrane trafficking in MDCK cells
- PMID: 9647644
- PMCID: PMC2133007
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.141.7.1503
The SNARE machinery is involved in apical plasma membrane trafficking in MDCK cells
Abstract
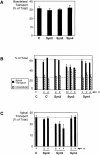
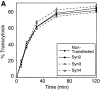
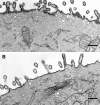
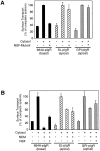
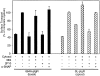
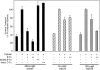
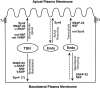
We have investigated the controversial involvement of components of the SNARE (soluble N-ethyl maleimide-sensitive factor [NSF] attachment protein [SNAP] receptor) machinery in membrane traffic to the apical plasma membrane of polarized epithelial (MDCK) cells. Overexpression of syntaxin 3, but not of syntaxins 2 or 4, caused an inhibition of TGN to apical transport and apical recycling, and leads to an accumulation of small vesicles underneath the apical plasma membrane. All other tested transport steps were unaffected by syntaxin 3 overexpression. Botulinum neurotoxin E, which cleaves SNAP-23, and antibodies against alpha-SNAP inhibit both TGN to apical and basolateral transport in a reconstituted in vitro system. In contrast, we find no evidence for an involvement of N-ethyl maleimide-sensitive factor in TGN to apical transport, whereas basolateral transport is NSF-dependent. We conclude that syntaxin 3, SNAP-23, and alpha-SNAP are involved in apical membrane fusion. These results demonstrate that vesicle fusion with the apical plasma membrane does not use a mechanism that is entirely unrelated to other cellular membrane fusion events, but uses isoforms of components of the SNARE machinery, which suggests that they play a role in providing specificity to polarized membrane traffic.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Raft association of SNAP receptors acting in apical trafficking in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Mar 30;96(7):3734-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.7.3734. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10097106 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstitution of transcytosis in SLO-permeabilized MDCK cells: existence of an NSF-dependent fusion mechanism with the apical surface of MDCK cells.EMBO J. 1996 Apr 1;15(7):1471-81. EMBO J. 1996. PMID: 8612570 Free PMC article.
-
Different requirements for NSF, SNAP, and Rab proteins in apical and basolateral transport in MDCK cells.Cell. 1995 May 19;81(4):571-80. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90078-0. Cell. 1995. PMID: 7758111
-
A new beat for the SNARE drum.Trends Cell Biol. 1998 Jun;8(6):215-8. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(98)01272-0. Trends Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9695844 Review.
-
SNAREs and membrane fusion in the Golgi apparatus.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998 Aug 14;1404(1-2):9-31. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(98)00044-5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998. PMID: 9714710 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of syntaxins in the specificity of vesicle targeting in polarized epithelial cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Dec;16(12):5784-92. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-07-0661. Epub 2005 Oct 5. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 16207812 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella enterica serovar typhi modulates cell surface expression of its receptor, the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator, on the intestinal epithelium.Infect Immun. 2002 Nov;70(11):6416-23. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.11.6416-6423.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 12379722 Free PMC article.
-
MYO5B, STX3, and STXBP2 mutations reveal a common disease mechanism that unifies a subset of congenital diarrheal disorders: A mutation update.Hum Mutat. 2018 Mar;39(3):333-344. doi: 10.1002/humu.23386. Epub 2018 Jan 17. Hum Mutat. 2018. PMID: 29266534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apical targeting of syntaxin 3 is essential for epithelial cell polarity.J Cell Biol. 2006 Jun 19;173(6):937-48. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200603132. J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16785322 Free PMC article.
-
Myosin vb is associated with plasma membrane recycling systems.Mol Biol Cell. 2001 Jun;12(6):1843-57. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.6.1843. Mol Biol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11408590 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acharya U, Jacobs R, Peters JM, Watson N, Farquhar MG, Malhotra V. The formation of Golgi stacks from vesiculated Golgi membranes requires two distinct fusion events. Cell. 1995;82:895–904. - PubMed
-
- Apodaca G, Aroeti B, Tang K, Mostov KE. Brefeldin-A inhibits the delivery of the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor to the basolateral surface of MDCK cells. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:20380–20385. - PubMed

