Kinesin light chains are essential for axonal transport in Drosophila
- PMID: 9548722
- PMCID: PMC2148443
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.141.2.443
Kinesin light chains are essential for axonal transport in Drosophila
Abstract
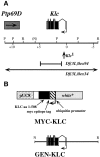
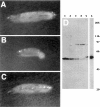
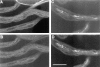
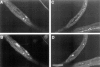
Kinesin is a heterotetramer composed of two 115-kD heavy chains and two 58-kD light chains. The microtubule motor activity of kinesin is performed by the heavy chains, but the functions of the light chains are poorly understood. Mutations were generated in the Drosophila gene Kinesin light chain (Klc), and the phenotypic consequences of loss of Klc function were analyzed at the behavioral and cellular levels. Loss of Klc function results in progressive lethargy, crawling defects, and paralysis followed by death at the end of the second larval instar. Klc mutant axons contain large aggregates of membranous organelles in segmental nerve axons. These aggregates, or organelle jams (Hurd, D.D., and W.M. Saxton. 1996. Genetics. 144: 1075-1085), contain synaptic vesicle precursors as well as organelles that may be transported by kinesin, kinesin-like protein 68D, and cytoplasmic dynein, thus providing evidence that the loss of Klc function blocks multiple pathways of axonal transport. The similarity of the Klc and Khc (. Cell 64:1093-1102; Hurd, D.D., and W.M. Saxton. 1996. Genetics 144: 1075-1085) mutant phenotypes indicates that KLC is essential for kinesin function, perhaps by tethering KHC to intracellular cargos or by activating the kinesin motor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Kinesin mutations cause motor neuron disease phenotypes by disrupting fast axonal transport in Drosophila.Genetics. 1996 Nov;144(3):1075-85. doi: 10.1093/genetics/144.3.1075. Genetics. 1996. PMID: 8913751 Free PMC article.
-
Defective kinesin heavy chain behavior in mouse kinesin light chain mutants.J Cell Biol. 1999 Sep 20;146(6):1277-88. doi: 10.1083/jcb.146.6.1277. J Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10491391 Free PMC article.
-
Cayman ataxia protein caytaxin is transported by kinesin along neurites through binding to kinesin light chains.J Cell Sci. 2009 Nov 15;122(Pt 22):4177-85. doi: 10.1242/jcs.048579. Epub 2009 Oct 27. J Cell Sci. 2009. PMID: 19861499
-
Conventional kinesin: Biochemical heterogeneity and functional implications in health and disease.Brain Res Bull. 2016 Sep;126(Pt 3):347-353. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2016.06.009. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Brain Res Bull. 2016. PMID: 27339812 Review.
-
The axonal transport of mitochondria.J Cell Sci. 2005 Dec 1;118(Pt 23):5411-9. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02745. J Cell Sci. 2005. PMID: 16306220 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An organelle gatekeeper function for Caenorhabditis elegans UNC-16 (JIP3) at the axon initial segment.Genetics. 2013 May;194(1):143-61. doi: 10.1534/genetics.112.147348. Genetics. 2013. PMID: 23633144 Free PMC article.
-
Huntingtin-mediated axonal transport requires arginine methylation by PRMT6.Cell Rep. 2021 Apr 13;35(2):108980. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108980. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 33852844 Free PMC article.
-
Kinesin-II is required for axonal transport of choline acetyltransferase in Drosophila.J Cell Biol. 1999 Nov 1;147(3):507-18. doi: 10.1083/jcb.147.3.507. J Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10545496 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms controlling the trafficking, localization, and abundance of presynaptic Ca2+ channels.Front Mol Neurosci. 2023 Jan 13;15:1116729. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.1116729. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36710932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynein light chain regulates axonal trafficking and synaptic levels of Bassoon.J Cell Biol. 2009 Apr 20;185(2):341-55. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200807155. J Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19380881 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beushausen S, Kladakis A, Jaffe H. Kinesin light chains: identification and characterization of a family of proteins from the optic lobe of the squid Loligo pealii. . DNA Cell Biol. 1993;12:901–909. - PubMed
-
- Bier E, Vaessin H, Shepherd S, Lee K, McCall K, Barbel S, Ackerman L, Carretto R, Uemura T, Grell E, et al. Searching for pattern and mutation in the Drosophilagenome with a P-lacZ vector. Genes Dev. 1989;3:1273–1287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

