Turnover of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes in HIV-1 infection as measured by Ki-67 antigen
- PMID: 9547340
- PMCID: PMC2212238
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.187.8.1295
Turnover of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes in HIV-1 infection as measured by Ki-67 antigen
Abstract
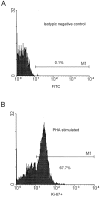
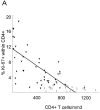
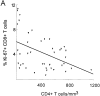
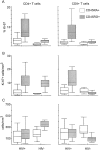
We investigated CD4+ and CD8+ T cell turnover in both healthy and HIV-1-infected adults by measuring the nuclear antigen Ki-67 specific for cell proliferation. The mean growth fraction, corresponding to the expression of Ki-67, was 1.1% for CD4(+) T cells and 1.0% in CD8(+) T cells in healthy adults, and 6.5 and 4.3% in HIV-1-infected individuals, respectively. Analysis of CD45RA+ and CD45RO+ T cell subsets revealed a selective expansion of the CD8+ CD45RO+ subset in HIV-1-positive individuals. On the basis of the growth fraction, we derived the potential doubling time and the daily turnover of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. In HIV-1-infected individuals, the mean potential doubling time of T cells was five times shorter than that of healthy adults. The mean daily turnover of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in HIV-1-infected individuals was increased 2- and 6-fold, respectively, with more than 40-fold interindividual variation. In patients with <200 CD4+ counts, CD4+ turnover dropped markedly, whereas CD8+ turnover remained elevated. The large variations in CD4+ T cell turnover might be relevant to individual differences in disease progression.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Distinct alterations in the distribution of CD45RO+ T-cell subsets in HIV-2 compared with HIV-1 infection.AIDS. 1994 Dec;8(12):1663-8. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199412000-00004. AIDS. 1994. PMID: 7888114
-
Increased numbers of primed activated CD8+CD38+CD45RO+ T cells predict the decline of CD4+ T cells in HIV-1-infected patients.AIDS. 1996 Jul;10(8):827-34. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199607000-00005. AIDS. 1996. PMID: 8828739
-
T-cell division in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-1 infection is mainly due to immune activation: a longitudinal analysis in patients before and during highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART).Blood. 2000 Jan 1;95(1):249-55. Blood. 2000. PMID: 10607709 Clinical Trial.
-
Increased proliferation within T lymphocyte subsets of HIV-infected adolescents.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2002 Nov 20;18(17):1301-10. doi: 10.1089/088922202320886343. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2002. PMID: 12487818
-
Comprehensive Mass Cytometry Analysis of Cell Cycle, Activation, and Coinhibitory Receptors Expression in CD4 T Cells from Healthy and HIV-Infected Individuals.Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2017 Jan;92(1):21-32. doi: 10.1002/cyto.b.21502. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2017. PMID: 27997758 Review.
Cited by
-
Progenitor and terminal subsets of CD8+ T cells cooperate to contain chronic viral infection.Science. 2012 Nov 30;338(6111):1220-5. doi: 10.1126/science.1229620. Science. 2012. PMID: 23197535 Free PMC article.
-
Divergent kinetics of proliferating T cell subsets in simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) infection: SIV eliminates the "first responder" CD4+ T cells in primary infection.J Virol. 2013 Jun;87(12):7032-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00027-13. Epub 2013 Apr 17. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23596288 Free PMC article.
-
Adrenaline-induced mobilization of T cells in HIV-infected patients.Clin Exp Immunol. 2000 Jan;119(1):115-22. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2000.01102.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10606972 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of T- and B-lymphocyte turnover in a natural host of simian immunodeficiency virus.J Virol. 2008 Feb;82(3):1084-93. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02197-07. Epub 2007 Nov 21. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18032490 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of peaks of virus load to simian immunodeficiency virus pathogenesis.J Virol. 2002 Mar;76(5):2573-8. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.5.2573-2578.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11836438 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fauci AS, Schnittman SM, Poli G, Koening S, Pantaleo G. Immunopathogenic mechanisms in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. Ann Intern Med. 1991;114:678–693. - PubMed
-
- Margolick JB. Changes in T and non-T lymphocyte subsets following seroconversion to HIV-1: stable CD3+and declining CD3 populations suggest regulatory responses linked to loss of CD4 lymphocytes. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1993;6:153–161. - PubMed
-
- Margolick JB, Munoz A, Donnenberg AD, Park LP, Galai N, Giorgi JV, O'Gorman MRG, Ferbas J. Failure of T-cell homeostatis preceding AIDS in HIV-1 infection. Nat Med. 1995;1:1674–1680. - PubMed
-
- Piatak M, Saag MS, Yang LC, Clark SJ, Kappes JC, Luk K-C, Hahn BH, Shaw GM, Lifson JD. High levels of HIV-1 in plasma during all stages of infection determined by competitive PCR. Science. 1993;259:1749–1754. - PubMed
-
- Pantaleo G, Graziosi C, Fauci AS. New concepts in the immunopathogenesis of human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:327–335. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

