Formation and function of the Rbl2p-beta-tubulin complex
- PMID: 9488492
- PMCID: PMC108890
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.3.1757
Formation and function of the Rbl2p-beta-tubulin complex
Abstract
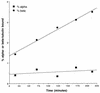
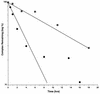
The yeast protein Rbl2p suppresses the deleterious effects of excess beta-tubulin as efficiently as does alpha-tubulin. Both in vivo and in vitro, Rbl2p forms a complex with beta-tubulin that does not contain alpha-tubulin, thus defining a second pool of beta-tubulin in the cell. Formation of the complex depends upon the conformation of beta-tubulin. Newly synthesized beta-tubulin can bind to Rbl2p before it binds to alpha-tubulin. Rbl2p can also bind beta-tubulin from the alpha/beta-tubulin heterodimer, apparently by competing with alpha-tubulin. The Rbl2p-beta-tubulin complex has a half-life of approximately 2.5 h and is less stable than the alpha/beta-tubulin heterodimer. The results of our experiments explain both how excess Rbl2p can rescue cells overexpressing beta-tubulin and how it can be deleterious in a wild-type background. They also suggest that the Rbl2p-beta-tubulin complex is part of a cellular mechanism for regulating the levels and dimerization of tubulin chains.
Figures


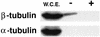
Similar articles
-
Function of tubulin binding proteins in vivo.Genetics. 2000 Sep;156(1):69-80. doi: 10.1093/genetics/156.1.69. Genetics. 2000. PMID: 10978276 Free PMC article.
-
Protection from free beta-tubulin by the beta-tubulin binding protein Rbl2p.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Jan;22(1):138-47. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.1.138-147.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11739729 Free PMC article.
-
Rbl2p, a yeast protein that binds to beta-tubulin and participates in microtubule function in vivo.Cell. 1995 Aug 11;82(3):425-34. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90431-x. Cell. 1995. PMID: 7634332
-
Tubulins in Aspergillus nidulans.Fungal Genet Biol. 2004 Apr;41(4):420-7. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2003.11.013. Fungal Genet Biol. 2004. PMID: 14998525 Review.
-
[The stathmin-tubulin interaction and the regulation of the microtubule assembly].Pathol Biol (Paris). 2003 Feb;51(1):33-8. doi: 10.1016/s0369-8114(02)00324-3. Pathol Biol (Paris). 2003. PMID: 12628290 Review. French.
Cited by
-
The structure of tubulin-binding cofactor A from Leishmania major infers a mode of association during the early stages of microtubule assembly.Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2015 May;71(Pt 5):539-46. doi: 10.1107/S2053230X15000990. Epub 2015 Apr 21. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2015. PMID: 25945706 Free PMC article.
-
Function of tubulin binding proteins in vivo.Genetics. 2000 Sep;156(1):69-80. doi: 10.1093/genetics/156.1.69. Genetics. 2000. PMID: 10978276 Free PMC article.
-
Protection from free beta-tubulin by the beta-tubulin binding protein Rbl2p.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Jan;22(1):138-47. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.1.138-147.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11739729 Free PMC article.
-
Dissociation of the tubulin dimer is extremely slow, thermodynamically very unfavorable, and reversible in the absence of an energy source.Mol Biol Cell. 2002 Jun;13(6):2120-31. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e01-10-0089. Mol Biol Cell. 2002. PMID: 12058074 Free PMC article.
-
Consequences of defective tubulin folding on heterodimer levels, mitosis and spindle morphology in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2006 Jun;173(2):635-46. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.055160. Epub 2006 Apr 2. Genetics. 2006. PMID: 16582437 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Archer J E, Vega L R, Solomon F. Rbl2p, a yeast protein that binds to β-tubulin and participates in microtubule function in vivo. Cell. 1995;82:425–434. - PubMed
-
- Campo R, Fontalba A, Sanchez L, Zabala J. A 14kDa release factor is involved in GTP-dependent beta-tubulin folding. FEBS Lett. 1994;353:162–166. - PubMed
-
- Compton, K., and F. Solomon. Unpublished results.
-
- Detrich H W, Williams R C. Reversible dissociation of the alpha-beta dimer of tubulin from bovine brain. Biochemistry. 1978;17:3900–3907. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
