Bone-specific expression of the alpha chain of the nascent polypeptide-associated complex, a coactivator potentiating c-Jun-mediated transcription
- PMID: 9488446
- PMCID: PMC108844
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.3.1312
Bone-specific expression of the alpha chain of the nascent polypeptide-associated complex, a coactivator potentiating c-Jun-mediated transcription
Abstract
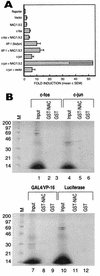
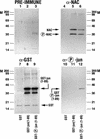
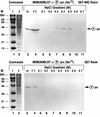
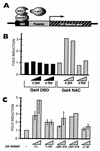
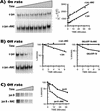
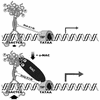
The alpha chain of the nascent polypeptide-associated complex (alpha-NAC) coactivator was shown to potentiate the activity of the homodimeric c-Jun activator, while transcription mediated by the c-Fos/c-Jun heterodimer was unaffected. The use of deletion mutants in pull-down assays revealed that alpha-NAC interacted with amino acids 1 to 89 of the c-Jun protein and that the coactivator could interact with both the unphosphorylated and the serine 73-phosphorylated form of c-Jun. N-terminal-deleted c-Jun protein failed to interact with alpha-NAC in mammalian two-hybrid assays, while mutant c-Jun proteins lacking the leucine zipper or the basic domain retained interaction with alpha-NAC in vivo. Kinetics studies with purified c-Jun homodimer and recombinant alpha-NAC proteins allowed determination of the mechanism of coactivation by alpha-NAC: the coactivator stabilized the AP-1 complex formed by the c-Jun homodimer on its DNA recognition sequence through an eightfold reduction in the dissociation constant (kd) of the complex. This effect of alpha-NAC was specific, because alpha-NAC could not stabilize the interactions of JunB or Sp1 with their cognate binding sites. Interestingly, the expression of alpha-NAC was first detected at 14.5 to 15 days postconception, concomitantly with the onset of ossification during embryogenesis. The alpha-NAC protein was specifically expressed in differentiated osteoblasts at the centers of ossification. Thus, the alpha-NAC gene product exhibits the properties of a developmentally regulated, bone-specific transcriptional coactivator.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Activation of the JNK-AP-1 signal transduction pathway is associated with pathogenesis and progression of human osteosarcomas.Bone. 2003 Apr;32(4):364-71. doi: 10.1016/s8756-3282(03)00026-7. Bone. 2003. PMID: 12689679
-
Integrin-linked kinase regulates the nuclear entry of the c-Jun coactivator alpha-NAC and its coactivation potency.J Biol Chem. 2004 Oct 15;279(42):43893-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M406310200. Epub 2004 Aug 6. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15299025
-
Transcriptional coactivators potentiating AP-1 function in bone.Front Biosci. 1998 Aug 1;3:d838-48. doi: 10.2741/a327. Front Biosci. 1998. PMID: 9682038 Review.
-
The alpha chain of the nascent polypeptide-associated complex functions as a transcriptional coactivator.Mol Cell Biol. 1998 Mar;18(3):1303-11. doi: 10.1128/MCB.18.3.1303. Mol Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9488445 Free PMC article.
-
c-Jun, at the crossroad of the signaling network.Protein Cell. 2011 Nov;2(11):889-98. doi: 10.1007/s13238-011-1113-3. Epub 2011 Dec 17. Protein Cell. 2011. PMID: 22180088 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NACA as a potential cellular target of hepatitis B virus preS1 protein.Dig Dis Sci. 2005 Jun;50(6):1156-60. doi: 10.1007/s10620-005-2724-4. Dig Dis Sci. 2005. PMID: 15986874
-
BTF3 sustains cancer stem-like phenotype of prostate cancer via stabilization of BMI1.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 May 28;38(1):227. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1222-z. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31138311 Free PMC article.
-
The beta Subunit of Nascent Polypeptide Associated Complex Plays A Role in Flowers and Siliques Development of Arabidopsis thaliana.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 17;21(6):2065. doi: 10.3390/ijms21062065. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32192231 Free PMC article.
-
Characterisation of the nascent polypeptide-associated complex in fission yeast.Mol Biol Rep. 2007 Dec;34(4):275-81. doi: 10.1007/s11033-006-9043-5. Epub 2007 Jan 9. Mol Biol Rep. 2007. PMID: 17211518
-
alphaNAC requires an interaction with c-Jun to exert its transcriptional coactivation.Gene Expr. 2002;10(5-6):255-62. doi: 10.3727/000000002783992433. Gene Expr. 2002. PMID: 12450217 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angel P, Karin M. The role of Jun, Fos and the AP-1 complex in cell proliferation and transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991;1072:129–157. - PubMed
-
- Arias J, Alberts A S, Brindle P, Claret F X, Smeal T, Karin M, Feramisco J, Montminy M. Activation of cAMP and mitogen responsive genes relies on a common nuclear factor. Nature. 1994;370:226–229. - PubMed
-
- Briggs M R, Kadonaga J T, Bell S P, Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986;234:47–52. - PubMed
-
- Candeliere G A, Prud’homme J, St-Arnaud R. Differential stimulation of Fos and Jun family members by calcitriol in osteoblastic cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1991;5:1780–1788. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
