Ezrin/radixin/moesin (ERM) proteins bind to a positively charged amino acid cluster in the juxta-membrane cytoplasmic domain of CD44, CD43, and ICAM-2
- PMID: 9472040
- PMCID: PMC2141743
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.140.4.885
Ezrin/radixin/moesin (ERM) proteins bind to a positively charged amino acid cluster in the juxta-membrane cytoplasmic domain of CD44, CD43, and ICAM-2
Abstract
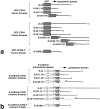
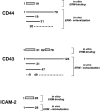
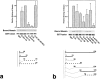
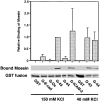
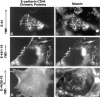
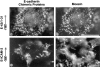
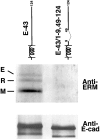
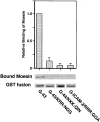
CD44 has been identified as a membrane-binding partner for ezrin/radixin/moesin (ERM) proteins, plasma membrane/actin filament cross-linkers. ERM proteins, however, are not necessarily colocalized with CD44 in tissues, but with CD43 and ICAM-2 in some types of cells. We found that glutathione-S-transferase fusion proteins with the cytoplasmic domain of CD43 and ICAM-2, as well as CD44, bound to moesin in vitro. The regions responsible for the in vitro binding of CD43 and CD44 to moesin were narrowed down to their juxta-membrane 20-30-amino acid sequences in the cytoplasmic domain. These sequences and the cytoplasmic domain of ICAM-2 (28 amino acids) were all characterized by the positively charged amino acid clusters. When E-cadherin chimeric molecules bearing these positively charged amino acid clusters of CD44, CD43, or ICAM-2 were expressed in mouse L fibroblasts, they were co-concentrated with ERM proteins at microvilli, whereas those lacking these clusters were diffusely distributed on the cell surface. The specific binding of ERM proteins to the juxta-membrane positively charged amino acid clusters of CD44, CD43, and ICAM-2 was confirmed by immunoprecipitation and site-directed mutagenesis. From these findings, we conclude that ERM proteins bind to integral membrane proteins bearing a positively charged amino acid cluster in their juxta-membrane cytoplasmic domain.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Direct involvement of ezrin/radixin/moesin (ERM)-binding membrane proteins in the organization of microvilli in collaboration with activated ERM proteins.J Cell Biol. 1999 Jun 28;145(7):1497-509. doi: 10.1083/jcb.145.7.1497. J Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10385528 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation mechanism of ERM (ezrin/radixin/moesin) protein/plasma membrane association: possible involvement of phosphatidylinositol turnover and Rho-dependent signaling pathway.J Cell Biol. 1996 Oct;135(1):37-51. doi: 10.1083/jcb.135.1.37. J Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8858161 Free PMC article.
-
A novel serine-rich motif in the intercellular adhesion molecule 3 is critical for its ezrin/radixin/moesin-directed subcellular targeting.J Biol Chem. 2002 Mar 22;277(12):10400-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110694200. Epub 2002 Jan 9. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11784723
-
Regulation of cortical structure by the ezrin-radixin-moesin protein family.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1999 Feb;11(1):109-16. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(99)80013-1. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10047517 Review.
-
[ERM (ezrin/radixin/moesin) as crosslinkers between actin filaments and plasma membranes].Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 1996 Sep;41(12 Suppl):1899-905. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 1996. PMID: 8890653 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Modulation of T cell immune functions by the prostaglandin E(2) - cAMP pathway in chronic inflammatory states.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 May;166(2):411-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01800.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22141738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Open conformation of ezrin bound to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and to F-actin revealed by neutron scattering.J Biol Chem. 2012 Oct 26;287(44):37119-33. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.380972. Epub 2012 Aug 26. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22927432 Free PMC article.
-
Activated ezrin promotes cell migration through recruitment of the GEF Dbl to lipid rafts and preferential downstream activation of Cdc42.Mol Biol Cell. 2007 Aug;18(8):2935-48. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e06-11-1031. Epub 2007 May 30. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17538024 Free PMC article.
-
The Ig cell adhesion molecule Basigin controls compartmentalization and vesicle release at Drosophila melanogaster synapses.J Cell Biol. 2007 Jun 4;177(5):843-55. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200701111. J Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17548512 Free PMC article.
-
CD95 (APO-1/Fas) linkage to the actin cytoskeleton through ezrin in human T lymphocytes: a novel regulatory mechanism of the CD95 apoptotic pathway.EMBO J. 2000 Oct 2;19(19):5123-34. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.19.5123. EMBO J. 2000. PMID: 11013215 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amieva MR, Wilgenbuns KK, Furthmayr H. Radixin is a component of hepatocyte microvilli in situ. Exp Cell Res. 1994;210:140–144. - PubMed
-
- Andréoli C, Martin M, Le-Borgne R, Reggio H, Mangeat P. Ezrin has properties to self-associate at the plasma membrane. J Cell Sci. 1994;107:2509–2521. - PubMed
-
- Arpin M, Algrain M, Louvard D. Membrane-actin microfilament connections: an increasing diversity of players related to band 4.1. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994;6:136–141. - PubMed
-
- Bennett V. The spectrin-actin junction of erythrocyte membrane skeletons. Biochem Biophys Acta. 1989;988:107–121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

