Caveolin-1 and -2 in the exocytic pathway of MDCK cells
- PMID: 9472032
- PMCID: PMC2141752
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.140.4.795
Caveolin-1 and -2 in the exocytic pathway of MDCK cells
Abstract
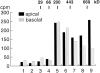
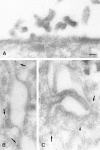
We have studied the biosynthesis and transport of the endogenous caveolins in MDCK cells. We show that in addition to homooligomers of caveolin-1, heterooligomeric complexes of caveolin-1 and -2 are formed in the ER. The oligomers become larger, increasingly detergent insoluble, and phosphorylated on caveolin-2 during transport to the cell surface. In the TGN caveolin-1/-2 heterooligomers are sorted into basolateral vesicles, whereas larger caveolin-1 homooligomers are targeted to the apical side. Caveolin-1 is present on both the apical and basolateral plasma membrane, whereas caveolin-2 is enriched on the basolateral surface where caveolae are present. This suggests that caveolin-1 and -2 heterooligomers are involved in caveolar biogenesis in the basolateral plasma membrane. Anti-caveolin-1 antibodies inhibit the apical delivery of influenza virus hemagglutinin without affecting basolateral transport of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein. Thus, we suggest that caveolin-1 homooligomers play a role in apical transport.
Figures





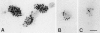
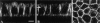
Similar articles
-
VIP36, a novel component of glycolipid rafts and exocytic carrier vesicles in epithelial cells.EMBO J. 1994 Apr 1;13(7):1729-40. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06437.x. EMBO J. 1994. PMID: 8157011 Free PMC article.
-
[Identification of signals and mechanisms of sorting of plasma membrane proteins in intestinal epithelial cells].J Soc Biol. 1999;193(2):131-4. J Soc Biol. 1999. PMID: 10451345 French.
-
Transport of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein to the cell surface is signal mediated in polarized and nonpolarized cells.J Cell Biol. 1996 May;133(3):543-58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.133.3.543. J Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8636230 Free PMC article.
-
VIP21-Caveolin, a protein of the trans-Golgi network and caveolae.FEBS Lett. 1994 Jun 6;346(1):88-91. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00466-8. FEBS Lett. 1994. PMID: 8206165 Review.
-
Caveolae and caveolins.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996 Aug;8(4):542-8. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(96)80033-0. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8791446 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of caveolin in trabecular meshwork cells and its possible implication in pathogenesis of primary open angle glaucoma.Mol Vis. 2011;17:2878-88. Epub 2011 Nov 9. Mol Vis. 2011. PMID: 22128235 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases-The Role of Endothelial Dysfunction.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Aug 8;14(16):1722. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14161722. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39202210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction of membrane/lipid rafts with the cytoskeleton: impact on signaling and function: membrane/lipid rafts, mediators of cytoskeletal arrangement and cell signaling.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Feb;1838(2):532-45. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2013.07.018. Epub 2013 Jul 27. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 23899502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Galectin-4 and sulfatides in apical membrane trafficking in enterocyte-like cells.J Cell Biol. 2005 May 9;169(3):491-501. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200407073. J Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15883199 Free PMC article.
-
Protein oligomerization modulates raft partitioning and apical sorting of GPI-anchored proteins.J Cell Biol. 2004 Nov 22;167(4):699-709. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200407094. J Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15557121 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beckers CJM, Keller DS, Balch WE. Semi-intact cells permeable to macromolecules: Use in reconstitution of protein transport from the endoplasmatic reticulum to the Golgi complex. Cell. 1987;50:523–534. - PubMed
-
- Bravo, R. 1984. Two-dimensional Gel Electrophoresis: A Guide for the Beginner. In Two-dimensional Gel Electrophoresis of Proteins. J.E. Celis and R. Bravo, editors. Academic Press Inc., Orlando, FL. 3–36.
-
- Dietzen DJ, Hastings WR, Lublin DM. Caveolin is palmitoylated on multiple cystein residues. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:6838–6842. - PubMed
-
- Fra AM, Williamson E, Simons K, Parton RG. Detergent-insoluble glycolipid microdomains in lymphocytes in the absence of caveolae. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:30745–30748. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

