Selection of virus variants and emergence of virus escape mutants after immunization with an epitope vaccine
- PMID: 9445041
- PMCID: PMC124619
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.2.1403-1410.1998
Selection of virus variants and emergence of virus escape mutants after immunization with an epitope vaccine
Abstract
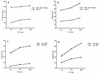
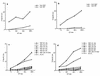
In this report, we assessed the evolution of the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) response induced by an epitope vaccine. In two macaques immunized with a mixture of lipopeptides derived from simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) Nef and Gag proteins, CTL responses were directed against the same, single epitope of the Nef protein (amino acids 128 to 137) presenting an alanine at position 136 (Nef 128-137/136A). However, after 5 months of SIV infection, peripheral blood mononuclear cells from both macaques lost their ability to be stimulated by autologous SIV-infected cells while still retaining their capacity to generate cytotoxic responses after specific Nef 128-137/136A peptide stimulation. The sequences of the pathogenic viral isolate used for the challenge showed a mixture of several variants. Within the Nef epitopic sequence from amino acids 128 to 137, 82% of viral variants expressed the epitopic peptide Nef 128-137/136A; the remaining variants presented a threonine at position 136 (Nef 128-137/136T). In contrast, sequence analysis of cloned proviral DNA obtained from both macaques 5 months after SIV challenge showed a different pattern of quasi-species variants; 100% of clones presented a threonine at position 136 (Nef 128-137/136T), suggesting the disappearance of viral variants with an alanine at this position under antiviral pressure exerted by Nef 128-137/136A-specific CTLs. In addition, 12 months after SIV challenge, six of eight clones from one macaque presented a glutamic acid at position 131 (Nef 128-137/131E+136T), which was not found in the infecting isolate. Furthermore, CTLs generated very early after SIV challenge were able to lyse cells sensitized with the Nef 128-137/136A epitope. In contrast, lysis was significantly less effective or even did not occur when either the selected peptide Nef 128-137/136T or the escape variant peptide Nef 128-137/131E+136T was used in a target cell sensitization assay. Dose analysis of peptides used to sensitize target cells as well as a major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-peptide stability assay suggested that the selected peptide Nef 128-137/136T has an altered capacity to bind to the MHC. These data suggest that CTL pressure leads to the selection of viral variants and to the emergence of escape mutants and supports the fact that immunization should elicit broad CTL responses.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Temporal loss of Nef-epitope CTL recognition following macaque lipopeptide immunization and SIV challenge.Virology. 2000 Dec 20;278(2):551-61. doi: 10.1006/viro.2000.0671. Virology. 2000. PMID: 11118377
-
Simian immunodeficiency virus as a model for vaccination against HIV. Induction in rhesus macaques of GAG- or NEF-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes by lipopeptides.J Immunol. 1994 Mar 1;152(5):2530-7. J Immunol. 1994. PMID: 8133061
-
A long-term follow-up of an HIV type 1-infected patient reveals a coincidence of Nef-directed cytotoxic T lymphocyte effectors and high incidence of epitope-deleted variants.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2001 Sep 1;17(13):1265-71. doi: 10.1089/088922201750461320. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2001. PMID: 11559426
-
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef epitopes recognized in HLA-A2 transgenic mice in response to DNA and peptide immunization.Virology. 2000 Jul 20;273(1):112-9. doi: 10.1006/viro.2000.0360. Virology. 2000. PMID: 10891413
-
Mechanisms of HIV protein degradation into epitopes: implications for vaccine design.Viruses. 2014 Aug 21;6(8):3271-92. doi: 10.3390/v6083271. Viruses. 2014. PMID: 25196483 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diversity of escape variant mutations in Simian virus 40 large tumor antigen (SV40 Tag) epitopes selected by cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) clones.Virology. 2007 Jul 20;364(1):155-68. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2007.02.007. Epub 2007 Mar 21. Virology. 2007. PMID: 17368499 Free PMC article.
-
CD8(+) lymphocytes from simian immunodeficiency virus-infected rhesus macaques recognize 14 different epitopes bound by the major histocompatibility complex class I molecule mamu-A*01: implications for vaccine design and testing.J Virol. 2001 Jan;75(2):738-49. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.2.738-749.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11134287 Free PMC article.
-
Expansion and exhaustion of T-cell responses during mutational escape from long-term viral control in two DNA/modified vaccinia virus Ankara-vaccinated and simian-human immunodeficiency virus SHIV-89.6P-challenged macaques.J Virol. 2008 Apr;82(8):4149-53. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02242-07. Epub 2008 Jan 30. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18234787 Free PMC article.
-
Extraepitopic compensatory substitutions partially restore fitness to simian immunodeficiency virus variants that escape from an immunodominant cytotoxic-T-lymphocyte response.J Virol. 2004 Mar;78(5):2581-5. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.5.2581-2585.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 14963161 Free PMC article.
-
Consequences of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte escape: common escape mutations in simian immunodeficiency virus are poorly recognized in naive hosts.J Virol. 2004 Sep;78(18):10064-73. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.18.10064-10073.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15331739 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aubertin, A. M. Personal communication.
-
- Bertoletti A, Sette A, Chisari F V, Penna A, Levrero M, De Carli M, Fiaccadori F, Ferrari C. Natural variants of cytotoxic epitopes are T-cell receptor antagonists for antiviral cytotoxic T cells. Nature (London) 1994;369:407–410. - PubMed
-
- Borrow P, Lewicki H, Wei X, Horwitz M S, Peffer N, Meyers H, Nelson J A, Gairin J E, Hahn B H, Oldstone M B A, Shaw G M. Antiviral pressure exerted by HIV-1-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) during primary infection demonstrated by rapid selection of CTL escape virus. Nat Med. 1997;3:205–211. - PubMed
-
- Bourgault I, Chirat F, Tartar A, Lévy J P, Guillet J G, Venet A. Simian immunodeficiency virus as model for vaccination against HIV. Induction in rhesus macaques of GAG- or NEF-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes by lipopeptides. J Immunol. 1994;152:2530–2537. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

