A new system for stringent, high-titer vesicular stomatitis virus G protein-pseudotyped retrovirus vector induction by introduction of Cre recombinase into stable prepackaging cell lines
- PMID: 9445007
- PMCID: PMC124585
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.2.1115-1121.1998
A new system for stringent, high-titer vesicular stomatitis virus G protein-pseudotyped retrovirus vector induction by introduction of Cre recombinase into stable prepackaging cell lines
Abstract
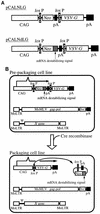
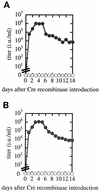
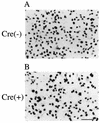
We report here on stable prepackaging cell lines which can be converted into packaging cell lines for high-titer vesicular stomatitis virus G protein (VSV-G)-pseudotyped retrovirus vectors by the introduction of Cre recombinase-expressing adenovirus. The generated prepackaging cell lines constitutively express the gag-pol genes and contain an inducible transcriptional unit for the VSV-G gene. From this unit, the introduced Cre recombinase excised both a neomycin resistance (Neo(r)) gene and a poly(A) signal flanked by a tandem pair of loxP sequences and induced transcription of the VSV-G gene from the same promoter as had been used for Neo(r) expression. By inserting an mRNA-destabilizing signal into the 3' untranslated region of the Neo(r) gene to reduce the amount of Neo(r) transcript, we were able efficiently to select the clones capable of inducing VSV-G at high levels. Without the introduction of Cre recombinase, these cell lines produce neither VSV-G nor any detectable infectious virus at all, even after the transduction of a murine leukemia virus-based retrovirus vector encoding beta-galactosidase. They reproducibly produced high-titer virus stocks of VSV-G-pseudotyped retrovirus (1.0 x 10(6) infectious units/ml) from 3 days after the introduction of Cre recombinase. We also present evidence that VSV-G-producing cells are still fully susceptible to transduction by VSV-G pseudotypes. However, in this vector-producing system, which regulates VSV-G pseudotype production in an all-or-none manner, the integration of vector DNA into packaging cell lines would be minimized. We further show that heparin significantly inhibits retransduction of VSV-G pseudotypes in the culture fluids of packaging cell lines, leading to a two- to fourfold increase in the yield of the pseudotypes after induction. This vector-producing system was very stable and should be advantageous in human gene therapy.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Inducible, high-level production of infectious murine leukemia retroviral vector particles pseudotyped with vesicular stomatitis virus G envelope protein.Hum Gene Ther. 1995 Sep;6(9):1203-13. doi: 10.1089/hum.1995.6.9-1203. Hum Gene Ther. 1995. PMID: 8527479
-
A stable human-derived packaging cell line for production of high titer retrovirus/vesicular stomatitis virus G pseudotypes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Oct 15;93(21):11400-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.21.11400. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996. PMID: 8876147 Free PMC article.
-
High-titer human immunodeficiency virus type 1-based vector systems for gene delivery into nondividing cells.J Virol. 1998 Nov;72(11):8873-83. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.11.8873-8883.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9765432 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of high-titer pseudotyped retroviral vectors with very broad host range.Methods Cell Biol. 1994;43 Pt A:99-112. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60600-7. Methods Cell Biol. 1994. PMID: 7823872 Review.
-
Lentiviral Vector Pseudotypes: Precious Tools to Improve Gene Modification of Hematopoietic Cells for Research and Gene Therapy.Viruses. 2020 Sep 11;12(9):1016. doi: 10.3390/v12091016. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32933033 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lentiviral Vector Bioprocessing.Viruses. 2021 Feb 9;13(2):268. doi: 10.3390/v13020268. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33572347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of SARS pseudovirus cell entry by lactoferrin binding to heparan sulfate proteoglycans.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23710. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023710. Epub 2011 Aug 22. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21887302 Free PMC article.
-
Fate of HIV-1 cDNA intermediates during reverse transcription is dictated by transcription initiation site of virus genomic RNA.Sci Rep. 2015 Dec 3;5:17680. doi: 10.1038/srep17680. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26631448 Free PMC article.
-
Heparin binds to murine leukemia virus and inhibits Env-independent attachment and infection.J Virol. 2002 Jul;76(14):6909-18. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.14.6909-6918.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12072492 Free PMC article.
-
Sequences in the cytoplasmic tail of the gibbon ape leukemia virus envelope protein that prevent its incorporation into lentivirus vectors.J Virol. 2001 May;75(9):4129-38. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.9.4129-4138.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11287562 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bassin R H, Ruscetti S, Ali I, Haapala D K, Rein A. Normal DBA/2 mouse cells synthesize a glycoprotein which interferes with MCF virus infection. Virology. 1982;123:139–151. - PubMed
-
- Beck E, Ludwig G, Auerswald E A, Reiss B, Schaller H. Nucleotide sequence and exact localization of the neomycin phosphotransferase gene from transposon Tn5. Gene. 1982;19:327–336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

