Evidence for covalent modification of the nuclear dot-associated proteins PML and Sp100 by PIC1/SUMO-1
- PMID: 9412458
- PMCID: PMC2132645
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.139.7.1621
Evidence for covalent modification of the nuclear dot-associated proteins PML and Sp100 by PIC1/SUMO-1
Abstract
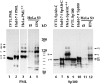
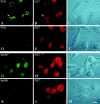
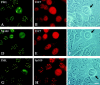
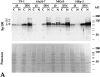
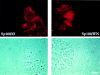
PML and Sp100 proteins are associated with nuclear domains, known as nuclear dots (NDs). They were discovered in the context of leukemic transformation and as an autoantigen in primary biliary cirrhosis, respectively. Both proteins are expressed in the form of many COOH-terminally spliced variants, and their expression is enhanced by interferons (IFN). The recent finding that PIC1/SUMO-1, a small ubiquitin-like protein, is covalently linked to the RanGAP1 protein of the nuclear pore complex and also binds PML in yeast cells led us to determine whether PML is covalently modified by PIC1/SUMO-1 and whether the same is true for Sp100. We found an immune reaction of PML and Sp100 proteins with a PIC1/SUMO-1-specific monoclonal antibody by immunoblotting when using cell extracts prepared from stably transfected cells inducibly expressing one isoform of each protein as well as from nontransfected cells. In contrast, both proteins did not react when synthesized in vitro. Immunofluorescence staining showed that PIC1/SUMO-1 colocalized with Sp100 and PML in NDs except in mitotic cells, in which PML and Sp100 are dissociated. Cell fractionation and immunoblotting demonstrated that PIC1/SUMO-1 immunoreactive Sp100 in IFN-treated and untreated cells was exclusively nuclear, whereas nonmodified Sp100 was also found in the cytoplasm. Taken together, these data strongly suggest covalent modification of specific nuclear isoforms of Sp100 and PML by PIC1/SUMO-1. This modification may play a regulatory role in ND structure, composition, and function.
Figures

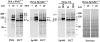



Similar articles
-
Cellular localization, expression, and structure of the nuclear dot protein 52.J Cell Biol. 1997 Jul 28;138(2):435-48. doi: 10.1083/jcb.138.2.435. J Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9230084 Free PMC article.
-
Herpes virus induced proteasome-dependent degradation of the nuclear bodies-associated PML and Sp100 proteins.Oncogene. 1999 Jan 28;18(4):935-41. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202366. Oncogene. 1999. PMID: 10023669
-
Small ubiquitin-related modifiers: A novel and independent class of autoantigens in primary biliary cirrhosis.Hepatology. 2005 Mar;41(3):609-16. doi: 10.1002/hep.20619. Hepatology. 2005. PMID: 15726652
-
Autoantibodies against "nuclear dots" in primary biliary cirrhosis.Semin Liver Dis. 1997 Feb;17(1):71-8. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1007184. Semin Liver Dis. 1997. PMID: 9089912 Review.
-
Nuclear dots: actors on many stages.Immunobiology. 1997 Dec;198(1-3):307-31. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(97)80051-4. Immunobiology. 1997. PMID: 9442402 Review.
Cited by
-
PML Body Component Sp100A Restricts Wild-Type Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Infection.J Virol. 2022 Apr 27;96(8):e0027922. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00279-22. Epub 2022 Mar 30. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35353002 Free PMC article.
-
Replication of ICP0-null mutant herpes simplex virus type 1 is restricted by both PML and Sp100.J Virol. 2008 Mar;82(6):2661-72. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02308-07. Epub 2007 Dec 26. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18160441 Free PMC article.
-
Viral and cellular factors that target the promyelocytic leukemia oncogenic domains strongly activate a glucocorticoid-responsive promoter.J Virol. 2001 Jun;75(11):5391-7. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.11.5391-5397.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11333923 Free PMC article.
-
Desumoylation activity of Axam, a novel Axin-binding protein, is involved in downregulation of beta-catenin.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Jun;22(11):3803-19. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.11.3803-3819.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11997515 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of SUMO-1 modification of neuronal proteins containing consensus SUMOylation motifs.Neurosci Lett. 2008 May 9;436(2):239-44. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2008.03.029. Epub 2008 Mar 15. Neurosci Lett. 2008. PMID: 18400391 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahn M-J, Nason-Burchenal K, Moasser MM, Dmitrovsky E. Growth suppression of acute promyelocytic leukemia cells having increased expression of the non-rearranged alleles: RARα or PML. Oncogene. 1995;10:2307–2314. - PubMed
-
- Aso T, Lane WS, Conaway JW, Conaway RC. Elongin (SIII): a multisubunit regulator of elongation by RNA polymerase II. Science. 1995;269:1439–1443. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

