mRNA capping enzyme is recruited to the transcription complex by phosphorylation of the RNA polymerase II carboxy-terminal domain
- PMID: 9407025
- PMCID: PMC316800
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.11.24.3319
mRNA capping enzyme is recruited to the transcription complex by phosphorylation of the RNA polymerase II carboxy-terminal domain
Abstract
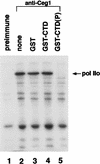
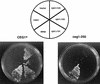
Capping of mRNA occurs shortly after transcription initiation, preceding other mRNA processing events such as mRNA splicing and polyadenylation. To determine the mechanism of coupling between transcription and capping, we tested for a physical interaction between capping enzyme and the transcription machinery. Capping enzyme is not stably associated with basal transcription factors or the RNA polymerase II (Pol II) holoenzyme. However, capping enzyme can directly and specifically interact with the phosphorylated form of the RNA polymerase carboxy-terminal domain (CTD). This association occurs in the context of the transcription initiation complex and is blocked by the CTD-kinase inhibitor H8. Furthermore, conditional truncation mutants of the Pol II CTD are lethal when combined with a capping enzyme mutant. Our results provide in vitro and in vivo evidence that capping enzyme is recruited to the transcription complex via phosphorylation of the RNA polymerase CTD.
Figures

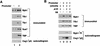
Comment in
-
Transcription units as RNA processing units.Genes Dev. 1997 Dec 15;11(24):3279-85. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.24.3279. Genes Dev. 1997. PMID: 9407022 Review. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
hnRNP U inhibits carboxy-terminal domain phosphorylation by TFIIH and represses RNA polymerase II elongation.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Oct;19(10):6833-44. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.10.6833. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10490622 Free PMC article.
-
Different phosphorylated forms of RNA polymerase II and associated mRNA processing factors during transcription.Genes Dev. 2000 Oct 1;14(19):2452-60. doi: 10.1101/gad.824700. Genes Dev. 2000. PMID: 11018013 Free PMC article.
-
5'-Capping enzymes are targeted to pre-mRNA by binding to the phosphorylated carboxy-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II.Genes Dev. 1997 Dec 15;11(24):3306-18. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.24.3306. Genes Dev. 1997. PMID: 9407024 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II plays central roles in the integrated events of eucaryotic gene expression.J Biochem. 2007 May;141(5):601-8. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvm090. Epub 2007 Apr 3. J Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17405796 Review.
-
Coupling mRNA processing with transcription in time and space.Nat Rev Genet. 2014 Mar;15(3):163-75. doi: 10.1038/nrg3662. Epub 2014 Feb 11. Nat Rev Genet. 2014. PMID: 24514444 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase control of the initiation-to-elongation switch of RNA polymerase II.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012 Nov;19(11):1108-15. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2399. Epub 2012 Oct 14. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 23064645 Free PMC article.
-
Participation of the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II in exon definition during pre-mRNA splicing.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Nov;20(21):8290-301. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.21.8290-8301.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11027297 Free PMC article.
-
Flavivirus methyltransferase: a novel antiviral target.Antiviral Res. 2008 Oct;80(1):1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2008.05.003. Epub 2008 Jun 5. Antiviral Res. 2008. PMID: 18571739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The conserved foot domain of RNA pol II associates with proteins involved in transcriptional initiation and/or early elongation.Genetics. 2011 Dec;189(4):1235-48. doi: 10.1534/genetics.111.133215. Epub 2011 Sep 27. Genetics. 2011. PMID: 21954159 Free PMC article.
-
Cdk9 regulates a promoter-proximal checkpoint to modulate RNA polymerase II elongation rate in fission yeast.Nat Commun. 2018 Feb 7;9(1):543. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03006-4. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29416031 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cadena DL, Dahmus ME. Messenger RNA synthesis in mammalian cells is catalyzed by the phosphorylated form of RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:12468–12474. - PubMed
-
- Colot HV, Stutz F, Rosbash M. The yeast splicing factor Mud13 is a commitment complex component and corresponds to CBP20, the small subunit of the nuclear cap-binding complex. Genes & Dev. 1996;10:1699–1708. - PubMed
-
- Dantonel JC, Murthy KGK, Manley JL, Tora L. Transcription factor TFIID recruits factor CPSF for formation of 3′ end of mRNA. Nature. 1997;389:399–402. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
