Major histocompatibility complex class I molecules modulate activation threshold and early signaling of T cell antigen receptor-gamma/delta stimulated by nonpeptidic ligands
- PMID: 9362537
- PMCID: PMC2199143
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.186.10.1769
Major histocompatibility complex class I molecules modulate activation threshold and early signaling of T cell antigen receptor-gamma/delta stimulated by nonpeptidic ligands
Abstract
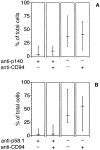
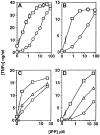
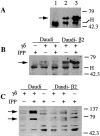
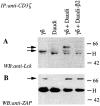
Killer cell inhibitory receptors and CD94-NKG2-A/B heterodimers are major histocompatibility complex class I-specific inhibitory receptors expressed by natural killer cells, T cell antigen receptor (TCR)-gamma/delta cells, and a subset of TCR-alpha/beta cells. We studied the functional interaction between TCR-gamma/delta and CD94, this inhibitory receptor being expressed on the majority of gamma/delta T cells. When engaged by human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen class I molecules, CD94 downmodulates activation of human TCR-gamma/delta by phosphorylated ligands. CD94-mediated inhibition is more effective at low than at high doses of TCR ligand, which may focus T cell responses towards antigen-presenting cells presenting high amounts of antigen. CD94 engagement has major effects on TCR signaling cascade. It facilitates recruitment of SHP-1 phosphatase to TCR-CD3 complex and affects phosphorylation of Lck and ZAP-70 kinase, but not of CD3 zeta chain upon TCR triggering. These events may cause abortion of proximal TCR-mediated signaling and set a higher TCR activation threshold.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Specific engagement of the CD94/NKG2-A killer inhibitory receptor by the HLA-E class Ib molecule induces SHP-1 phosphatase recruitment to tyrosine-phosphorylated NKG2-A: evidence for receptor function in heterologous transfectants.Eur J Immunol. 1998 Apr;28(4):1280-91. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(199804)28:04<1280::AID-IMMU1280>3.0.CO;2-O. Eur J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9565368
-
CD94/NKG2 inhibitory receptor complex modulates both anti-viral and anti-tumoral responses of polyclonal phosphoantigen-reactive V gamma 9V delta 2 T lymphocytes.J Immunol. 1997 Dec 15;159(12):6009-17. J Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9550399
-
Expression of p58.2 or CD94/NKG2A inhibitory receptors in an NK-like cell line, YTINDY, leads to HLA Class I-mediated inhibition of cytotoxicity in the p58.2- but not the CD94/NKG2A-expressing transfectant.Cell Immunol. 2002 Sep;219(1):57-70. doi: 10.1016/s0008-8749(02)00578-6. Cell Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12473268
-
Structure and function of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I specific receptors expressed on human natural killer (NK) cells.Mol Immunol. 2002 Feb;38(9):637-60. doi: 10.1016/s0161-5890(01)00107-9. Mol Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11858820 Review.
-
Structure and function of the CD94 C-type lectin receptor complex involved in recognition of HLA class I molecules.Immunol Rev. 1997 Feb;155:165-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1997.tb00949.x. Immunol Rev. 1997. PMID: 9059892 Review.
Cited by
-
High resolution HLA analysis reveals independent class I haplotypes and amino-acid motifs protective for multiple sclerosis.Genes Immun. 2019 Apr;20(4):308-326. doi: 10.1038/s41435-017-0006-8. Epub 2018 Jan 8. Genes Immun. 2019. PMID: 29307888 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-induced disruption of proximal TCR-mediated signal transduction in tumor-infiltrating CD8+ lymphocytes inactivates antitumor effector phase.J Immunol. 2010 Dec 15;185(12):7133-40. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1001157. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 21127315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tissue distribution, antigen specificity and effector functions of gamma delta T cells in human diseases.Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2000;22(3):219-38. doi: 10.1007/s002810000043. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2000. PMID: 11116954 Review. No abstract available.
-
Uncoupling of T-cell effector functions by inhibitory killer immunoglobulin-like receptors.Blood. 2006 Jun 1;107(11):4449-57. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-06-2519. Epub 2006 Feb 9. Blood. 2006. PMID: 16469873 Free PMC article.
-
Human gamma delta T lymphocytes in HIV disease: effector functions and control by natural killer cell receptors.Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2000;22(3):251-63. doi: 10.1007/s002810000046. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2000. PMID: 11116956 Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Moretta A, Bottino C, Vitale M, Pende D, Biassoni R, Mingari MC, Moretta L. Receptors for HLA class-I molecules in human natural killer cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:619–648. - PubMed
-
- Lanier LL, Phillips JH. Inhibitory MHC class I receptors on NK cells and T cells. Immunol Today. 1996;17:86–91. - PubMed
-
- Colonna M. Natural killer cell receptors specific for MHC class I molecules. Curr Opin Immunol. 1996;8:101–107. - PubMed
-
- Long EO, Burshtyn DN, Clark WP, Peruzzi M, Rajagopalan S, Rojo S, Wagtmann N, Winter CC. Killer cell inhibitory receptors: diversity, specificity and function. Immunol Rev. 1997;155:135–144. - PubMed
-
- Lazetic S, Chang C, Houchins JP, Lanier LL, Phillips JP. Human natural killer cell receptors involved in MHC class I recognition are disulfide-linked heterodimers of CD94 and NKG2 subunits. J Immunol. 1996;157:4741–4745. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

