Topoisomerase IV, not gyrase, decatenates products of site-specific recombination in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 9334322
- PMCID: PMC316566
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.11.19.2580
Topoisomerase IV, not gyrase, decatenates products of site-specific recombination in Escherichia coli
Abstract
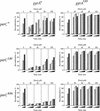
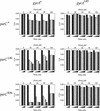
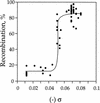
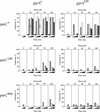
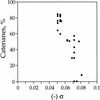
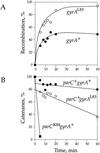
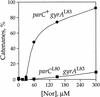
DNA replication and recombination generate intertwined DNA intermediates that must be decatenated for chromosome segregation to occur. We showed recently that topoisomerase IV (topo IV) is the only important decatenase of DNA replication intermediates in bacteria. Earlier results, however, indicated that DNA gyrase has the primary role in unlinking the catenated products of site-specific recombination. To address this discordance, we constructed a set of isogenic strains that enabled us to inhibit selectively with the quinolone norfloxacin topo IV, gyrase, both enzymes, or neither enzyme in vivo. We obtained identical results for the decatenation of the products of two different site-specific recombination enzymes, phage lambda integrase and transposon Tn3 resolvase. Norfloxacin blocked decatenation in wild-type strains, but had no effect in strains with drug-resistance mutations in both gyrase and topo IV. When topo IV alone was inhibited, decatenation was almost completely blocked. If gyrase alone were inhibited, most of the catenanes were unlinked. We showed that topo IV is the primary decatenase in vivo and that this function is dependent on the level of DNA supercoiling. We conclude that the role of gyrase in decatenation is to introduce negative supercoils into DNA, which makes better substrates for topo IV. We also discovered that topo IV has an unexpectedly strong DNA relaxation activity that, together with gyrase and topo I, is able to set the supercoiling levels in Escherichia coli.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Contrasting enzymatic activities of topoisomerase IV and DNA gyrase from Escherichia coli.J Biol Chem. 1996 Dec 6;271(49):31549-55. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.49.31549. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8940171
-
Roles of topoisomerases in maintaining steady-state DNA supercoiling in Escherichia coli.J Biol Chem. 2000 Mar 17;275(11):8103-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.11.8103. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10713132
-
Analysis of topoisomerase function in bacterial replication fork movement: use of DNA microarrays.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Aug 15;97(17):9419-24. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.17.9419. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10944214 Free PMC article.
-
[DNA supercoiling and topoisomerases in Escherichia coli].Rev Latinoam Microbiol. 1995 Jul-Sep;37(3):291-304. Rev Latinoam Microbiol. 1995. PMID: 8850348 Review. Spanish.
-
What makes a type IIA topoisomerase a gyrase or a Topo IV?Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Jun 21;49(11):6027-6042. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab270. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33905522 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
DNA supercoiling in bacteria: state of play and challenges from a viewpoint of physics based modeling.Front Microbiol. 2023 Oct 30;14:1192831. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1192831. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37965550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How topoisomerase IV can efficiently unknot and decatenate negatively supercoiled DNA molecules without causing their torsional relaxation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jun 2;44(10):4528-38. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw311. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27106058 Free PMC article.
-
emDNA - A Tool for Modeling Protein-decorated DNA Loops and Minicircles at the Base-pair Step Level.J Mol Biol. 2022 Jun 15;434(11):167558. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2022.167558. Epub 2022 Mar 24. J Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35341743 Free PMC article.
-
The ancestral role of ATP hydrolysis in type II topoisomerases: prevention of DNA double-strand breaks.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Aug;39(15):6327-39. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr258. Epub 2011 Apr 27. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21525132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing sensitivity to antibacterial topoisomerase II inhibitors.Curr Protoc Pharmacol. 2007 Dec;Chapter 3:Unit3.13. doi: 10.1002/0471141755.ph0313s39. Curr Protoc Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 21948169 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams DE, Bliska JB, Cozzarelli NR. Cre-lox recombination in E. coli cells: Mechanistic differences from the in vitro reaction. J Mol Biol. 1992a;226:661–673. - PubMed
-
- Adams DE, Shekhtman EM, Zechiedrich EL, Schmid MB, Cozzarelli NR. The role of topoisomerase IV in partitioning bacterial replicons and the structure of catenated intermediates in DNA replication. Cell. 1992b;71:277–288. - PubMed
-
- Belland RJ, Morrison SG, Ison C, Huang WM. Neisseria gonorrhoeae acquires mutations in analogous regions of gyrA and parC in fluoroquinolone-resistant isolates. Mol Microbiol. 1994;14:371–380. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin KR, Abola AP, Kanaar R, Cozzarelli NR. Contributions of supercoiling to Tn3 resolvase and phage mu gin site-specific recombination. J Mol Biol. 1996;256:50–65. - PubMed
-
- Bjornsti M-A. DNA topoisomerases. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1991;1:99–103.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
