Src-induced activation of inducible T cell kinase (ITK) requires phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity and the Pleckstrin homology domain of inducible T cell kinase
- PMID: 9326591
- PMCID: PMC23424
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.21.11227
Src-induced activation of inducible T cell kinase (ITK) requires phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity and the Pleckstrin homology domain of inducible T cell kinase
Abstract
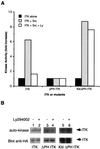
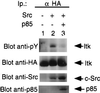
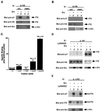
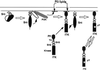
The Tec family of tyrosine kinases are involved in signals emanating from cytokine receptors, antigen receptors, and other lymphoid cell surface receptors. One family member, ITK (inducible T cell kinase), is involved in T cell activation and can be activated by the T cell receptor and the CD28 cell surface receptor. This stimulation of tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of ITK can be mimicked by the Src family kinase Lck. We have explored the mechanism of this requirement for Src family kinases in the activation of ITK. We found that coexpression of ITK and Src results in increased membrane association, tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of ITK, which could be blocked by inhibitors of the lipid kinase phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI 3-kinase) as well as overexpression of the p85 subunit of PI 3-kinase. Removal of the Pleckstrin homology domain (PH) of ITK resulted in a kinase that could no longer be induced to localize to the membrane or be activated by Src. The PH of ITK was also able to bind inositol phosphates phosphorylated at the D3 position. Membrane targeting of ITK without the PH recovered its ability to be activated by Src. These results suggest that ITK can be activated by a combination of Src and PI 3-kinase.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Keeping the (kinase) party going: SLP-76 and ITK dance to the beat.Sci STKE. 2007 Jul 24;2007(396):pe39. doi: 10.1126/stke.3962007pe39. Sci STKE. 2007. PMID: 17652306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The proline rich region of the Tec homology domain of ITK regulates its activity.FEBS Lett. 2002 Aug 14;525(1-3):53-8. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(02)03066-1. FEBS Lett. 2002. PMID: 12163161
-
Src-family tyrosine kinases, phosphoinositide 3-kinase and Gab1 regulate extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 activation induced by the type A endothelin-1 G-protein-coupled receptor.Biochem J. 2001 Nov 15;360(Pt 1):77-85. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3600077. Biochem J. 2001. PMID: 11695994 Free PMC article.
-
p56Lck and p59Fyn regulate CD28 binding to phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, growth factor receptor-bound protein GRB-2, and T cell-specific protein-tyrosine kinase ITK: implications for T-cell costimulation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 12;92(19):8891-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.19.8891. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995. PMID: 7568038 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical and genetic analyses of the Tec kinases Itk and Rlk/Txk.Biochem Soc Trans. 2001 Nov;29(Pt 6):863-7. doi: 10.1042/0300-5127:0290863. Biochem Soc Trans. 2001. PMID: 11709089 Review.
Cited by
-
Allele-sensitive mutant, Itkas, reveals that Itk kinase activity is required for Th1, Th2, Th17, and iNKT-cell cytokine production.Eur J Immunol. 2015 Aug;45(8):2276-85. doi: 10.1002/eji.201445087. Epub 2015 Jun 10. Eur J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25989458 Free PMC article.
-
Keeping the (kinase) party going: SLP-76 and ITK dance to the beat.Sci STKE. 2007 Jul 24;2007(396):pe39. doi: 10.1126/stke.3962007pe39. Sci STKE. 2007. PMID: 17652306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Tec family kinase Itk exists as a folded monomer in vivo.J Biol Chem. 2009 Oct 23;284(43):29882-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.003129. Epub 2009 Aug 28. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19717557 Free PMC article.
-
Tec kinases regulate T-lymphocyte development and function: new insights into the roles of Itk and Rlk/Txk.Immunol Rev. 2009 Mar;228(1):93-114. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00757.x. Immunol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19290923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Interleukin-2-Inducible T-Cell Kinase (ITK) Differentiates GVL and GVHD in Allo-HSCT.Front Immunol. 2020 Nov 26;11:593863. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.593863. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33324410 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gibson S, Leung B, Squire J A, Hill M, Arima N, Goss P, Hogg D, Mills G B. Blood. 1993;82:1561–1572. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka N, Asao H, Ohtani K, Nakamura M, Sugamura K. FEBS Lett. 1993;324:1–5. - PubMed
-
- Yamada N, Kawakami Y, Kimura H, Fukamachi H, Baier G, Altman A, Kato T, Inagi Y, Kawakami T. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993;192:231–240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

