Role of actin polymerization and adhesion to extracellular matrix in Rac- and Rho-induced cytoskeletal reorganization
- PMID: 9265656
- PMCID: PMC2138040
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.138.4.913
Role of actin polymerization and adhesion to extracellular matrix in Rac- and Rho-induced cytoskeletal reorganization
Abstract
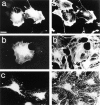
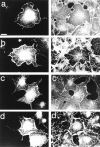
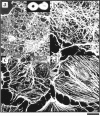
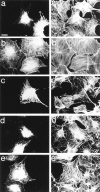
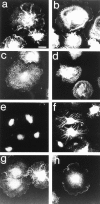
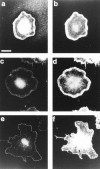
Most animal cells use a combination of actin-myosin-based contraction and actin polymerization- based protrusion to control their shape and motility. The small GTPase Rho triggers the formation of contractile stress fibers and focal adhesion complexes (Ridley, A.J., and A. Hall. 1992. Cell. 70:389-399) while a close relative, Rac, induces lamellipodial protrusions and focal complexes in the lamellipodium (Nobes, C.D., and A. Hall. 1995. Cell. 81:53-62; Ridley, A.J., H.F. Paterson, C.L. Johnston, D. Diekmann, and A. Hall. 1992. Cell. 70:401-410); the Rho family of small GTPases may thus play an important role in regulating cell movement. Here we explore the roles of actin polymerization and extracellular matrix in Rho- and Rac-stimulated cytoskeletal changes. To examine the underlying mechanisms through which these GTPases control F-actin assembly, fluorescently labeled monomeric actin, Cy3-actin, was introduced into serum-starved Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. Incorporation of Cy3- actin into lamellipodial protrusions is concomitant with F-actin assembly after activation of Rac, but Cy3-actin is not incorporated into stress fibers formed immediately after Rho activation. We conclude that Rac induces rapid actin polymerization in ruffles near the plasma membrane, whereas Rho induces stress fiber assembly primarily by the bundling of actin filaments. Activation of Rho or Rac also leads to the formation of integrin adhesion complexes. Integrin clustering is not required for the Rho-induced assembly of actin-myosin filament bundles, or for vinculin association with actin bundles, but is required for stress fiber formation. Integrin-dependent focal complex assembly is not required for the Rac-induced formation of lamellipodia or membrane ruffles. It appears, therefore, that the assembly of large integrin complexes is not required for most of the actin reorganization or cell morphology changes induced by Rac or Rho activation in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rho, rac, and cdc42 GTPases regulate the assembly of multimolecular focal complexes associated with actin stress fibers, lamellipodia, and filopodia.Cell. 1995 Apr 7;81(1):53-62. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90370-4. Cell. 1995. PMID: 7536630
-
Rho- and rac-dependent assembly of focal adhesion complexes and actin filaments in permeabilized fibroblasts: an essential role for ezrin/radixin/moesin proteins.J Cell Biol. 1997 Aug 25;138(4):927-38. doi: 10.1083/jcb.138.4.927. J Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9265657 Free PMC article.
-
Ras-related GTPases and the cytoskeleton.Mol Biol Cell. 1992 May;3(5):475-9. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.5.475. Mol Biol Cell. 1992. PMID: 1611153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Growth factor induced activation of Rho and Rac GTPases and actin cytoskeletal reorganization in human lens epithelial cells.Mol Vis. 2003 Jul 17;9:329-36. Mol Vis. 2003. PMID: 12876554
-
Regulation of phosphorylation pathways by p21 GTPases. The p21 Ras-related Rho subfamily and its role in phosphorylation signalling pathways.Eur J Biochem. 1996 Dec 1;242(2):171-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1996.0171r.x. Eur J Biochem. 1996. PMID: 8973630 Review.
Cited by
-
Fenestrated Endothelial Cells across Organs: Insights into Kidney Function and Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 22;25(16):9107. doi: 10.3390/ijms25169107. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Actin networks modulate heterogeneous NF-κB dynamics in response to TNFα.Elife. 2024 Aug 7;13:e86042. doi: 10.7554/eLife.86042. Elife. 2024. PMID: 39110005 Free PMC article.
-
Unravelling molecular dynamics in living cells: Fluorescent protein biosensors for cell biology.J Microsc. 2024 Feb 15:10.1111/jmi.13270. doi: 10.1111/jmi.13270. Online ahead of print. J Microsc. 2024. PMID: 38357769
-
Tff3 Deficiency Differentially Affects the Morphology of Male and Female Intestines in a Long-Term High-Fat-Diet-Fed Mouse Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 15;24(22):16342. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216342. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003531 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the integrin αVβ3- actin filaments axis in early osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells under cyclic tensile stress.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Oct 30;21(1):308. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-01027-7. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37904190 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bershadsky A, Chausovsky A, Becker E, Lyubimova A, Geiger B. Involvement of microtubules in the control of adhesion-dependent signal transduction. Curr Biol. 1996;6:1279–1289. - PubMed
-
- Bretcher MS. Getting membrane flow and the cytoskeleton to cooperate in moving cells. Cell. 1996;87:601–606. - PubMed
-
- Burridge K, Fath K. Focal contacts: transmembrane links between the extracellular matrix and the cytoskeleton. Bioessays. 1989;10:104–108. - PubMed
-
- Burridge K, Fath K, Kelly T, Nuckolls G, Turner C. Focal Adhesions: transmembrane junctions between the extracellular matrix and the cytoskeleton. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:487–525. - PubMed
-
- Burridge K, Nuckolls G, Otey C, Pavalko F, Simon K, Turner C. Actin membrane interaction in focal adhesions. Cell Differ Dev. 1990;32:337–342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

