Novel genes involved in endosomal traffic in yeast revealed by suppression of a targeting-defective plasma membrane ATPase mutant
- PMID: 9265642
- PMCID: PMC2138039
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.138.4.731
Novel genes involved in endosomal traffic in yeast revealed by suppression of a targeting-defective plasma membrane ATPase mutant
Abstract
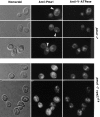
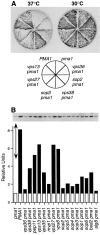
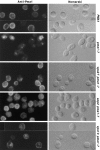
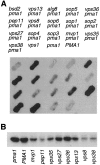
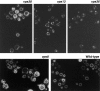
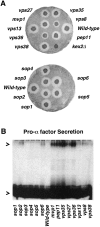
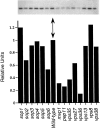
A novel genetic selection was used to identify genes regulating traffic in the yeast endosomal system. We took advantage of a temperature-sensitive mutant in PMA1, encoding the plasma membrane ATPase, in which newly synthesized Pma1 is mislocalized to the vacuole via the endosome. Diversion of mutant Pma1 from vacuolar delivery and rerouting to the plasma membrane is a major mechanism of suppression of pma1(ts). 16 independent suppressor of pma1 (sop) mutants were isolated. Identification of the corresponding genes reveals eight that are identical with VPS genes required for delivery of newly synthesized vacuolar proteins. A second group of SOP genes participates in vacuolar delivery of mutant Pma1 but is not essential for delivery of the vacuolar protease carboxypeptidase Y. Because the biosynthetic pathway to the vacuole intersects with the endocytic pathway, internalization of a bulk membrane endocytic marker FM 4-64 was assayed in the sop mutants. By this means, defective endosome-to-vacuole trafficking was revealed in a subset of sop mutants. Another subset of sop mutants displays perturbed trafficking between endosome and Golgi: impaired pro-alpha factor processing in these strains was found to be due to defective recycling of the trans-Golgi protease Kex2. One of these strains defective in Kex2 trafficking carries a mutation in SOP2, encoding a homologue of mammalian synaptojanin (implicated in synaptic vesicle endocytosis and recycling). Thus, cell surface delivery of mutant Pma1 can occur as a consequence of disturbances at several different sites in the endosomal system.
Figures



Similar articles
-
An endosome-to-plasma membrane pathway involved in trafficking of a mutant plasma membrane ATPase in yeast.Mol Biol Cell. 2000 Feb;11(2):579-92. doi: 10.1091/mbc.11.2.579. Mol Biol Cell. 2000. PMID: 10679016 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting of the yeast plasma membrane [H+]ATPase: a novel gene AST1 prevents mislocalization of mutant ATPase to the vacuole.J Cell Biol. 1995 Jan;128(1-2):39-49. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.1.39. J Cell Biol. 1995. PMID: 7822420 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin-mediated targeting of a mutant plasma membrane ATPase, Pma1-7, to the endosomal/vacuolar system in yeast.Mol Biol Cell. 2004 May;15(5):2401-9. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e03-10-0727. Epub 2004 Mar 12. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15020711 Free PMC article.
-
New Perspectives on SNARE Function in the Yeast Minimal Endomembrane System.Genes (Basel). 2020 Aug 6;11(8):899. doi: 10.3390/genes11080899. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32781543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The yeast Pma1 proton pump: a model for understanding the biogenesis of plasma membrane proteins.J Biol Chem. 2001 Aug 10;276(32):29613-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R100022200. Epub 2001 Jun 12. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11404364 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Synthetic genetic interactions with temperature-sensitive clathrin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Roles for synaptojanin-like Inp53p and dynamin-related Vps1p in clathrin-dependent protein sorting at the trans-Golgi network.Genetics. 2000 Jan;154(1):83-97. doi: 10.1093/genetics/154.1.83. Genetics. 2000. PMID: 10628971 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma membrane proton ATPase Pma1p requires raft association for surface delivery in yeast.Mol Biol Cell. 2001 Dec;12(12):4129-38. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.12.4129. Mol Biol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11739806 Free PMC article.
-
Heat shock response relieves ER stress.EMBO J. 2008 Apr 9;27(7):1049-59. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2008.42. Epub 2008 Mar 6. EMBO J. 2008. PMID: 18323774 Free PMC article.
-
ESCRT regulates surface expression of the Kir2.1 potassium channel.Mol Biol Cell. 2014 Jan;25(2):276-89. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E13-07-0394. Epub 2013 Nov 13. Mol Biol Cell. 2014. PMID: 24227888 Free PMC article.
-
A mutant plasma membrane ATPase, Pma1-10, is defective in stability at the yeast cell surface.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Jul 31;98(16):9104-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.161282998. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11481477 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong J, Patel S, Riddle P. Lysosomal sorting mutants of coronavirus E1 protein, a Golgi membrane protein. J Cell Sci. 1990;95:191–197. - PubMed
-
- Attree O, Olivos IM, Okabe I, Bailey LC, Nelson DL, Lewis RA, McInnes RR, Nussbaum RL. The Lowe's oculocerebrorenal syndrome gene encodes a protein highly homologous to inositol polyphosphate-5-phosphatase. Nature (Lond) 1992;358:239–242. - PubMed
-
- Benito B, Moreno E, Losario R. Half-life of plasma membrane ATPase and its activating system in resting yeast cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991;1063:265–268. - PubMed
-
- Burns N, Grimwade B, Ross-Macdonald PB, Choi E-Y, Finberg K, Roeder GS, Snyder M. Large-scale analysis of gene expression, protein localization, and gene disruption in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. . Genes Dev. 1994;8:1087–1105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

