Spontaneous cell fusion in macrophage cultures expressing high levels of the P2Z/P2X7 receptor
- PMID: 9245796
- PMCID: PMC2141639
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.138.3.697
Spontaneous cell fusion in macrophage cultures expressing high levels of the P2Z/P2X7 receptor
Erratum in
- J Cell Biol 1997 Oct 20;139(2):following 571
Abstract
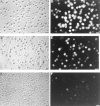
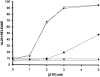
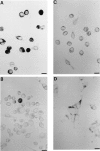
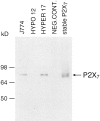
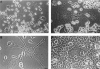
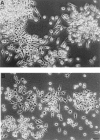
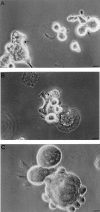
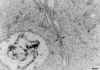
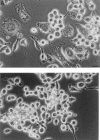
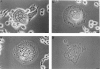
Mouse and human macrophages express a plasma membrane receptor for extracellular ATP named P2Z/P2X7. This molecule, recently cloned, is endowed with the intriguing property of forming an aqueous pore that allows transmembrane fluxes of hydrophylic molecules of molecular weight below 900. The physiological function of this receptor is unknown. In a previous study we reported experiments suggesting that the P2Z/P2X7 receptor is involved in the formation of macrophage-derived multinucleated giant cells (MGCs; Falzoni, S., M. Munerati, D. Ferrari, S. Spisani, S. Moretti, and F. Di Virgilio. 1995. J. Clin. Invest. 95:1207- 1216). We have selected several clones of mouse J774 macrophages that are characterized by either high or low expression of the P2Z/P2X7 receptor and named these clones P2Zhyper or P2Zhypo, respectively. P2Zhyper, but not P2Zhypo, cells grown to confluence in culture spontaneously fuse to form MGCs. As previously shown for human macrophages, fusion is inhibited by the P2Z/P2X7 blocker oxidized ATP. MGCs die shortly after fusion through a dramatic process of cytoplasmic sepimentation followed by fragmentation. These observations support our previous hypothesis that the P2Z/P2X7 receptor is involved in macrophage fusion.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Purinergic receptor modulation of lipopolysaccharide signaling and inducible nitric-oxide synthase expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages.J Biol Chem. 1998 Oct 16;273(42):27170-5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.42.27170. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9765236
-
ATP released by LPS increases nitric oxide production in raw 264.7 macrophage cell line via P2Z/P2X7 receptors.Neurochem Int. 1998 Sep;33(3):209-15. doi: 10.1016/s0197-0186(98)00025-4. Neurochem Int. 1998. PMID: 9759915
-
Partial agonists and antagonists reveal a second permeability state of human lymphocyte P2Z/P2X7 channel.Am J Physiol. 1998 Nov;275(5):C1224-31. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1998.275.5.C1224. Am J Physiol. 1998. PMID: 9814970
-
ATP receptors and giant cell formation.J Leukoc Biol. 1999 Nov;66(5):723-6. doi: 10.1002/jlb.66.5.723. J Leukoc Biol. 1999. PMID: 10577500 Review.
-
P2Z purinoceptors.Ciba Found Symp. 1996;198:71-83; discussion 83-90. doi: 10.1002/9780470514900.ch4. Ciba Found Symp. 1996. PMID: 8879819 Review.
Cited by
-
Hyaluronan fragments improve wound healing on in vitro cutaneous model through P2X7 purinoreceptor basal activation: role of molecular weight.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e48351. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048351. Epub 2012 Nov 16. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23173033 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the purinergic P2X7 receptor in inflammation.J Inflamm (Lond). 2007 Mar 16;4:5. doi: 10.1186/1476-9255-4-5. J Inflamm (Lond). 2007. PMID: 17367517 Free PMC article.
-
Multinucleated Giant Cells: Current Insights in Phenotype, Biological Activities, and Mechanism of Formation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Apr 11;10:873226. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.873226. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35478968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A cyclic pathway of P2 × 7, bradykinin, and dopamine receptor activation induces a sustained articular hyperalgesia in the knee joint of rats.Inflamm Res. 2018 Apr;67(4):301-314. doi: 10.1007/s00011-017-1122-7. Epub 2017 Dec 19. Inflamm Res. 2018. PMID: 29260240
-
Microglia at brain stab wounds express connexin 43 and in vitro form functional gap junctions after treatment with interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Mar 27;98(7):4190-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.051634298. Epub 2001 Mar 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11259646 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baricordi, O., D. Ferrari, L. Melchiorri, P. Chiozzi, S. Hanau, E. Chiari, M. Rubini, and F. Di Virgilio. 1996. An ATP-activated channel is involved in mitogenic stimulation of human T lymphocytes. Blood, 87:682–690. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard DK, McMillen S, Djeu JY. IFN-γ enhances sensitivity of human macrophages to extracellular ATP-mediated lysis. J Immunol. 1991;147:2579–2585. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard DK, Wei S, Duan C, Pericle F, Diaz JI, Djeu JY. Role of extracellular adenosine triphosphate in the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-mediated lysis of antigen presenting cells. Blood. 1995;11:3173–3182. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

