Daxx, a novel Fas-binding protein that activates JNK and apoptosis
- PMID: 9215629
- PMCID: PMC2989411
- DOI: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80294-9
Daxx, a novel Fas-binding protein that activates JNK and apoptosis
Abstract
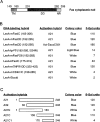
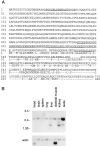
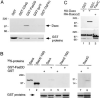
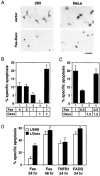
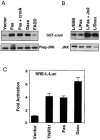
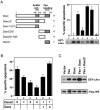
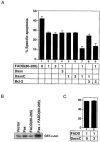
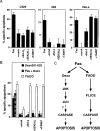
The Fas cell surface receptor induces apoptosis upon receptor oligomerization. We have identified a novel signaling protein, termed Daxx, that binds specifically to the Fas death domain. Overexpression of Daxx enhances Fas-mediated apoptosis and activates the Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway. A C-terminal portion of Daxx interacts with the Fas death domain, while a different region activates both JNK and apoptosis. The Fas-binding domain of Daxx is a dominant-negative inhibitor of both Fas-induced apoptosis and JNK activation, while the FADD death domain partially inhibits death but not JNK activation. The Daxx apoptotic pathway is sensitive to both Bcl-2 and dominant-negative JNK pathway components and acts cooperatively with the FADD pathway. Thus, Daxx and FADD define two distinct apoptotic pathways downstream of Fas.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ultraviolet radiation-induced apoptosis is mediated by Daxx.Neoplasia. 2002 Nov-Dec;4(6):486-92. doi: 10.1038/sj.neo.7900264. Neoplasia. 2002. PMID: 12407442 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting Fas signaling with an altered-specificity death-domain mutant: requirement of FADD binding for apoptosis but not Jun N-terminal kinase activation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Feb 16;96(4):1252-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.4.1252. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 9990010 Free PMC article.
-
Long form of cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein interacts with Daxx and prevents Fas-induced JNK activation.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003 Dec 12;312(2):426-33. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.10.144. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003. PMID: 14637155
-
Live and let die: regulatory mechanisms in Fas-mediated apoptosis.Cell Signal. 2003 Nov;15(11):983-92. doi: 10.1016/s0898-6568(03)00093-7. Cell Signal. 2003. PMID: 14499341 Review.
-
The Daxx enigma.Apoptosis. 2000 Jun;5(3):217-20. doi: 10.1023/a:1009696227420. Apoptosis. 2000. PMID: 11225842 Review.
Cited by
-
Daxx upregulation within the cytoplasm of reovirus-infected cells is mediated by interferon and contributes to apoptosis.J Virol. 2013 Mar;87(6):3447-60. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02324-12. Epub 2013 Jan 9. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23302889 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor suppressor protein Pdcd4 interacts with Daxx and modulates the stability of Daxx and the Hipk2-dependent phosphorylation of p53 at serine 46.Oncogenesis. 2013 Jan 14;2(1):e37. doi: 10.1038/oncsis.2012.37. Oncogenesis. 2013. PMID: 23536002 Free PMC article.
-
The Clinical Impact of Death Domain-Associated Protein and Holliday Junction Recognition Protein Expression in Cancer: Unmasking the Driving Forces of Neoplasia.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 26;15(21):5165. doi: 10.3390/cancers15215165. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37958340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulating Androgen Receptor Function in Prostate Cancer: Exploring the Diversity of Post-Translational Modifications.Cells. 2024 Jan 19;13(2):191. doi: 10.3390/cells13020191. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38275816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanistic insights into the oncolytic activity of vesicular stomatitis virus in cancer immunotherapy.Oncolytic Virother. 2015 Oct 15;4:157-67. doi: 10.2147/OV.S66079. eCollection 2015. Oncolytic Virother. 2015. PMID: 27512679 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abbas AK. Die and let live: eliminating dangerous lymphocytes. Cell. 1996;84:655–658. - PubMed
-
- Boldin MP, Goncharov TM, Goltsev YV, Wallach D. Involvement of MACH, a novel MORT1/FADD-interacting protease, in Fas/APO-1-and TNF receptor–induced cell death. Cell. 1996;85:803–815. - PubMed
-
- Boldin MP, Mett IL, Varfolomeev EE, Chumakov I, Shemer-Avni Y, Camonis JH, Wallach D. Self-association of the “death domains” of the p55 tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor and Fas/Apo1 prompts signalling for TNF and Fas/Apo1 effects. J. Biol. Chem. 1995a;270:387–391. - PubMed
-
- Boldin MP, Varfolomev EE, Pancer Z, Mett IL, Camonis JH, Wallach D. A novel protein that interacts with the death domain of Fas/APO1 contains a sequence motif related to the death domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1995b;270:7795–7798. - PubMed
-
- Brown PH, Chen TK, Birrer MJ. Mechanism of action of a dominant-negative mutant of c-Jun. Oncogene. 1994;9:791–799. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

