In vitro reconstitution of cortical actin assembly sites in budding yeast
- PMID: 9214384
- PMCID: PMC2139943
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.138.1.95
In vitro reconstitution of cortical actin assembly sites in budding yeast
Abstract
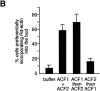
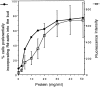
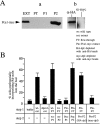
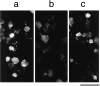
We have developed a biochemical approach for identifying the components of cortical actin assembly sites in polarized yeast cells, based on a permeabilized cell assay that we established for actin assembly in vitro. Previous analysis indicated that an activity associated with the cell cortex promotes actin polymerization in the bud. After inactivation by a chemical treatment, this activity can be reconstituted back to the permeabilized cells from a cytoplasmic extract. Fractionation of the extract revealed that the reconstitution depends on two sequentially acting protein factors. Bee1, a cortical actin cytoskeletal protein with sequence homology to Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein, is required for the first step of the reconstitution. This finding, together with the severe defects in actin organization associated with the bee1 null mutation, indicates that Bee1 protein plays a direct role in controlling actin polymerization at the cell cortex. The factor that acts in the second step of the reconstitution has been identified by conventional chromatography. It is composed of a novel protein, Pca1. Sequence analysis suggests that Pca1 has the potential to interact with SH3 domain-containing proteins and phospholipids.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Bee1, a yeast protein with homology to Wiscott-Aldrich syndrome protein, is critical for the assembly of cortical actin cytoskeleton.J Cell Biol. 1997 Feb 10;136(3):649-58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.136.3.649. J Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9024694 Free PMC article.
-
Direct involvement of yeast type I myosins in Cdc42-dependent actin polymerization.J Cell Biol. 2000 Jan 24;148(2):363-73. doi: 10.1083/jcb.148.2.363. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10648569 Free PMC article.
-
GCS1, an Arf guanosine triphosphatase-activating protein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is required for normal actin cytoskeletal organization in vivo and stimulates actin polymerization in vitro.Mol Biol Cell. 1999 Mar;10(3):581-96. doi: 10.1091/mbc.10.3.581. Mol Biol Cell. 1999. PMID: 10069805 Free PMC article.
-
Ras-related GTPases and the cytoskeleton.Mol Biol Cell. 1992 May;3(5):475-9. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.5.475. Mol Biol Cell. 1992. PMID: 1611153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pan1p: an actin director of endocytosis in yeast.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007;39(10):1760-4. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2006.12.001. Epub 2006 Dec 21. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17303466 Review.
Cited by
-
Eng1p, an endo-1,3-beta-glucanase localized at the daughter side of the septum, is involved in cell separation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Eukaryot Cell. 2002 Oct;1(5):774-86. doi: 10.1128/EC.1.5.774-786.2002. Eukaryot Cell. 2002. PMID: 12455695 Free PMC article.
-
SCAR is a primary regulator of Arp2/3-dependent morphological events in Drosophila.J Cell Biol. 2002 Feb 18;156(4):689-701. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200109057. Epub 2002 Feb 18. J Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11854309 Free PMC article.
-
A protein interaction map for cell polarity development.J Cell Biol. 2001 Aug 6;154(3):549-71. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200104057. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11489916 Free PMC article.
-
A two-tiered mechanism by which Cdc42 controls the localization and activation of an Arp2/3-activating motor complex in yeast.J Cell Biol. 2001 Oct 15;155(2):261-70. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200104094. Epub 2001 Oct 15. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11604421 Free PMC article.
-
Terry Lechler: the cytoskeleton is skin deep. Interview by Nicole LeBrasseur.J Cell Biol. 2007 Aug 13;178(4):546-7. doi: 10.1083/jcb.1784pi. J Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17698603 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

