Interleukin 8-stimulated phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase activity regulates the migration of human neutrophils independent of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases
- PMID: 9096344
- PMCID: PMC20320
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.7.3052
Interleukin 8-stimulated phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase activity regulates the migration of human neutrophils independent of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases
Abstract
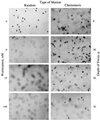
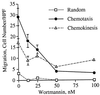
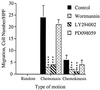
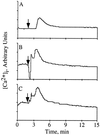
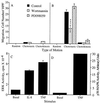
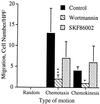
Chemoattractants and chemokines, such as interleukin 8 (IL-8), are defined by their ability to induce directed cell migration of responsive cells. The signal transduction pathway(s) leading to cell migration remain ill defined. We demonstrate that phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) activity, as determined by inhibition using wortmannin and LY294002, is required for IL-8-induced cell migration of human neutrophils. Recently we reported that IL-8 caused the activation of the Ras/Raf/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway in human neutrophils and that this activation was dependent on PI3K activity. The regulation of cell migration by IL-8 is independent of ERK kinase and ERK activation since the ERK kinase inhibitor PD098059 had no effect on IL-8-induced cell migration of human neutrophils. Additionally, activation of p38-mitogen-activated protein kinase is insufficient and activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase is unnecessary to induce cell migration of human neutrophils. Therefore, regulation of neutrophil migration appears to be largely independent of the activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinases. The data argue that PI3K activity plays a central role in multiple signal transduction pathways within the human neutrophil leading to distinct cell functions.
Figures
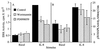
Similar articles
-
Comparison of the roles of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signal transduction in neutrophil effector function.Biochem J. 1998 Jan 1;329 ( Pt 1)(Pt 1):121-30. doi: 10.1042/bj3290121. Biochem J. 1998. PMID: 9405284 Free PMC article.
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase activation through Fc epsilon receptor I and stem cell factor receptor is differentially regulated by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and calcineurin in mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells.J Immunol. 1999 Feb 15;162(4):2087-94. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 9973482
-
Chemotactic peptide-induced activation of MEK-2, the predominant isoform in human neutrophils. Inhibition by wortmannin.J Biol Chem. 1996 Aug 30;271(35):21005-1011. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.35.21005. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8702863
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase is required for integrin-stimulated AKT and Raf-1/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway activation.Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Aug;17(8):4406-18. doi: 10.1128/MCB.17.8.4406. Mol Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9234699 Free PMC article.
-
Growth hormone stimulates phosphorylation and activation of elk-1 and expression of c-fos, egr-1, and junB through activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2.J Biol Chem. 1998 Nov 20;273(47):31327-36. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.47.31327. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9813041
Cited by
-
Differentiation, apoptosis, and function of human immature and mature myeloid cells: intracellular signaling mechanism.Int J Hematol. 2001 Jun;73(4):438-452. doi: 10.1007/BF02994005. Int J Hematol. 2001. PMID: 11503957 Review.
-
Comparison of doxycycline and minocycline in the inhibition of VEGF-induced smooth muscle cell migration.Neurochem Int. 2007 Feb;50(3):524-30. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2006.10.008. Epub 2006 Dec 4. Neurochem Int. 2007. PMID: 17145119 Free PMC article.
-
CXC chemokine receptors in the central nervous system: Role in cerebellar neuromodulation and development.J Neurovirol. 2002 Dec;8(6):559-72. doi: 10.1080/13550280290100932. J Neurovirol. 2002. PMID: 12476350 Review.
-
Inhibition of kinases impairs neutrophil activation and killing of Staphylococcus aureus.Biochem J. 1998 Apr 15;331 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):489-95. doi: 10.1042/bj3310489. Biochem J. 1998. PMID: 9531489 Free PMC article.
-
Pivotal role of IL-8 derived from the interaction between osteosarcoma and tumor-associated macrophages in osteosarcoma growth and metastasis via the FAK pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Feb 1;15(2):108. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06487-y. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38302407 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

