Expression of presenilin 1 and 2 (PS1 and PS2) in human and murine tissues
- PMID: 8922407
- PMCID: PMC6579112
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-23-07513.1996
Expression of presenilin 1 and 2 (PS1 and PS2) in human and murine tissues
Abstract
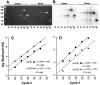
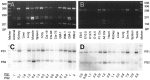
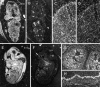
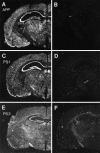
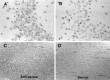
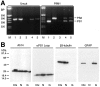
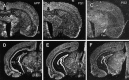
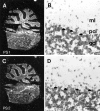
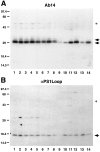
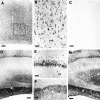
Mutations in genes encoding related proteins, termed presenilin 1 (PS1) and presenilin 2 (PS2), are linked to the majority of cases with early-onset familial Alzheimer's disease (FAD). To clarify potential function(s) of presenilins and relationships of presenilin expression to pathogenesis of AD, we examined the expression of PS1 and PS2 mRNA and PS1 protein in human and mouse. Semi-quantitative PCR of reverse-transcribed RNA (RT-PCR) analysis revealed that PS1 and PS2 mRNA are expressed ubiquitously and at comparable levels in most human and mouse tissues, including adult brain. However, PS1 mRNA is expressed at significantly higher levels in developing brain. In situ hybridization studies of mouse embryos revealed widespread expression of PS1 mRNA with a neural expression pattern that, in part, overlaps that reported for mRNA encoding specific Notch homologs. In situ hybridization analysis in adult mouse brain revealed that PS1 and PS2 mRNAs are enriched in neurons of the hippocampal formation and entorhinal cortex. Although PS1 and PS2 mRNA are expressed most prominently in neurons, lower but significant levels of PS1 and PS2 transcripts are also detected in white matter glial cells. Moreover, cultured neurons and astrocytes express PS1 and PS2 mRNAs. Using PS1-specific antibodies in immunoblot analysis, we demonstrate that PS1 accumulates as approximately 28 kDa N-terminal and approximately 18 kDa C-terminal fragments in brain. Immunocytochemical studies of mouse brain reveal that PS1 protein accumulates in a variety of neuronal populations with enrichment in somatodendritic and neuropil compartments.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Brain expression of presenilins in sporadic and early-onset, familial Alzheimer's disease.Mol Med. 2000 Oct;6(10):878-91. Mol Med. 2000. PMID: 11126202 Free PMC article.
-
Presenilin proteins undergo heterogeneous endoproteolysis between Thr291 and Ala299 and occur as stable N- and C-terminal fragments in normal and Alzheimer brain tissue.Neurobiol Dis. 1997;3(4):325-37. doi: 10.1006/nbdi.1997.0129. Neurobiol Dis. 1997. PMID: 9173929
-
Constitutive and cytokine-regulated expression of presenilin-1 and presenilin-2 genes in human neural cell lines.Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1999 Dec;25(6):492-503. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2990.1999.00209.x. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1999. PMID: 10632899
-
Presenilins and Alzheimer's disease: biological functions and pathogenic mechanisms.Prog Neurobiol. 2000 Mar;60(4):363-84. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0082(99)00033-7. Prog Neurobiol. 2000. PMID: 10670705 Review.
-
[Molecular cell biology of presenilins].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1999 Dec;114(6):337-46. doi: 10.1254/fpj.114.337. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1999. PMID: 10672594 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
A role for presenilins in autophagy revisited: normal acidification of lysosomes in cells lacking PSEN1 and PSEN2.J Neurosci. 2012 Jun 20;32(25):8633-48. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0556-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22723704 Free PMC article.
-
Presenilin-2 and Calcium Handling: Molecules, Organelles, Cells and Brain Networks.Cells. 2020 Sep 25;9(10):2166. doi: 10.3390/cells9102166. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32992716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human alpha-synuclein-harboring familial Parkinson's disease-linked Ala-53 --> Thr mutation causes neurodegenerative disease with alpha-synuclein aggregation in transgenic mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Jun 25;99(13):8968-73. doi: 10.1073/pnas.132197599. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12084935 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular signatures of neurodegeneration in the cortex of PS1/PS2 double knockout mice.Mol Neurodegener. 2008 Oct 3;3:14. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-3-14. Mol Neurodegener. 2008. PMID: 18834536 Free PMC article.
-
Presenilin 1 interacts with acetylcholinesterase and alters its enzymatic activity and glycosylation.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 May;28(9):2908-19. doi: 10.1128/MCB.02065-07. Epub 2008 Feb 25. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18299393 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alzheimer’s Disease Collaborative Group. The structure of the presenilin 1 (S182) gene and identification of six novel mutations in early onset AD families. Nat Genet. 1995;11:219–222. - PubMed
-
- Bendotti C, Forloni GL, Morgan RA, O’Hara BF, Oster-Granite ML, Reeves RH, Gearhart JD, Coyle JT. Neuroanatomical localization and quantification of amyloid precursor protein mRNA by in situ hybridization in the brains of normal, aneuploid, and lesioned mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1988;85:3628–3632. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boteva K, Vitek M, Mitsuda H, de Silva H, Xu P-T, Small G, Gilbert JR. Mutation analysis of presenilin 1 gene in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet. 1996;347:130–131. - PubMed
-
- Campion D, Flaman JM, Brice A, Hannequin D, Dubois B, Martin C, Moreau V, Charbonnier F, Didierjean O, Tardieu S, Penet C, Puel M, Pasquier F, Ledoze F, Bellis G, Calenda A, Heilig R, Martinez M, Mallet J, Bellis M, Clergetdarpoux F, Agid Y, Frebourg T. Mutations of the presenilin 1 gene in families with early-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Mol Genet. 1995;4:2373–2377. - PubMed
-
- Chapman J, Asherov A, Wang N, Treves TA, Korczyn AD, Goldfarb LG. Familial Alzheimer’s disease associated with S182 codon 286 mutation. Lancet. 1995;346:1040. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
