An essential role for p300/CBP in the cellular response to hypoxia
- PMID: 8917528
- PMCID: PMC24030
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.93.23.12969
An essential role for p300/CBP in the cellular response to hypoxia
Abstract
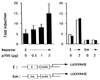
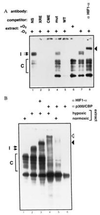
p300 and CBP are homologous transcription adapters targeted by the E1A oncoprotein. They participate in numerous biological processes, including cell cycle arrest, differentiation, and transcription activation. p300 and/or CBP (p300/CBP) also coactivate CREB. How they participate in these processes is not yet known. In a search for specific p300 binding proteins, we have cloned the intact cDNA for HIF-1 alpha. This transcription factor mediates hypoxic induction of genes encoding certain glycolytic enzymes, erythropoietin (Epo), and vascular endothelial growth factor. Hypoxic conditions lead to the formation of a DNA binding complex containing both HIF-1 alpha and p300/CBP. Hypoxia-induced transcription from the Epo promoter was specifically enhanced by ectopic p300 and inhibited by E1A binding to p300/CBP. Hypoxia-induced VEGF and Epo mRNA synthesis were similarly inhibited by E1A. Hence, p300/CBP-HIF complexes participate in the induction of hypoxia-responsive genes, including one (vascular endothelial growth factor) that plays a major role in tumor angiogenesis. Paradoxically, these data, to our knowledge for the first time, suggest that p300/ CBP are active in both transformation suppression and tumor development.
Figures

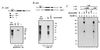
Similar articles
-
A family of transcriptional adaptor proteins targeted by the E1A oncoprotein.Nature. 1995 Mar 2;374(6517):81-4. doi: 10.1038/374081a0. Nature. 1995. PMID: 7870178
-
Activation of vascular endothelial growth factor gene transcription by hypoxia-inducible factor 1.Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Sep;16(9):4604-13. doi: 10.1128/MCB.16.9.4604. Mol Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8756616 Free PMC article.
-
V-SRC induces expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) and transcription of genes encoding vascular endothelial growth factor and enolase 1: involvement of HIF-1 in tumor progression.Cancer Res. 1997 Dec 1;57(23):5328-35. Cancer Res. 1997. PMID: 9393757
-
Erythropoietin gene regulation depends on heme-dependent oxygen sensing and assembly of interacting transcription factors.Kidney Int. 1997 Feb;51(2):548-52. doi: 10.1038/ki.1997.76. Kidney Int. 1997. PMID: 9027736 Review.
-
The coactivators p300 and CBP have different functions during the differentiation of F9 cells.J Mol Med (Berl). 1999 Jun;77(6):481-94. doi: 10.1007/s001099900021. J Mol Med (Berl). 1999. PMID: 10475063 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) by lysophosphatidic acid is dependent on interplay between p53 and Krüppel-like factor 5.J Biol Chem. 2013 Aug 30;288(35):25244-25253. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.489708. Epub 2013 Jul 23. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23880760 Free PMC article.
-
MGA2 is involved in the low-oxygen response element-dependent hypoxic induction of genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Sep;21(18):6161-9. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.18.6161-6169.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11509659 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia and oxidative stress in breast cancer. Hypoxia signalling pathways.Breast Cancer Res. 2001;3(5):313-7. doi: 10.1186/bcr313. Epub 2001 Jul 16. Breast Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11597320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GA-binding protein and p300 are essential components of a retinoic acid-induced enhanceosome in myeloid cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Apr;26(8):3060-70. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.8.3060-3070.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16581781 Free PMC article.
-
c-Jun and hypoxia-inducible factor 1 functionally cooperate in hypoxia-induced gene transcription.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Jan;22(1):12-22. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.1.12-22.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11739718 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shweiki D, Itin A, Soffer D, Keshet E. Nature (London) 1992;359:843–845. - PubMed
-
- Plate K H G, Breier G, Weich H A, Risau W. Nature (London) 1992;359:845–848. - PubMed
-
- Eckner R, Ewen M E, Newsome D, Gerdes M, DeCaprio J A, Bentley Lawrence J, Livingston D M. Genes Dev. 1994;8:869–884. - PubMed
-
- Arany Z, Sellers W R, Livingston D M, Eckner R. Cell. 1994;77:799–800. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

