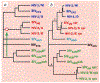
Gene acquisition in HIV and SIV
- PMID: 8857532
- PMCID: PMC9514223
- DOI: 10.1038/383586a0
Gene acquisition in HIV and SIV
Figures
Similar articles
-
Complex evolutionary history of primate lentiviral vpr genes.Virology. 1998 Jan 20;240(2):232-7. doi: 10.1006/viro.1997.8929. Virology. 1998. PMID: 9454696
-
Characterization of a novel simian immunodeficiency virus with a vpu gene from greater spot-nosed monkeys (Cercopithecus nictitans) provides new insights into simian/human immunodeficiency virus phylogeny.J Virol. 2002 Aug;76(16):8298-309. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.16.8298-8309.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12134035 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and comparison of recombinant simian immunodeficiency virus from drill (Mandrillus leucophaeus) and mandrill (Mandrillus sphinx) isolates.J Virol. 2003 Apr;77(8):4867-80. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.8.4867-4880.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12663793 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogeny and natural history of the primate lentiviruses, SIV and HIV.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1995 Dec;5(6):798-806. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(95)80014-v. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1995. PMID: 8745080 Review.
-
[Exchangeability of HIV/SIV regulatory genes].Uirusu. 1992 Dec;42(2):133-43. doi: 10.2222/jsv.42.133. Uirusu. 1992. PMID: 1295209 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Limelight on two HIV/SIV accessory proteins in macrophage infection: is Vpx overshadowing Vpr?Retrovirology. 2010 Apr 9;7:35. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-7-35. Retrovirology. 2010. PMID: 20380700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of Vpr and Vpx in modulating the virus-host cell relationship.Mol Aspects Med. 2010 Oct;31(5):398-406. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2010.05.002. Epub 2010 Jun 15. Mol Aspects Med. 2010. PMID: 20558198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
E3 Ubiquitin Ligases in Gammaherpesviruses and HIV: A Review of Virus Adaptation and Exploitation.Viruses. 2023 Sep 15;15(9):1935. doi: 10.3390/v15091935. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37766341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 vpr gene induces phenotypic effects similar to those of the DNA alkylating agent, nitrogen mustard.J Virol. 1997 May;71(5):3961-71. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.5.3961-3971.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 9094673 Free PMC article.
-
Features of Maternal HIV-1 Associated with Lack of Vertical Transmission.Open Virol J. 2017 Mar 23;11:8-14. doi: 10.2174/1874357901710011008. eCollection 2017. Open Virol J. 2017. PMID: 28458735 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

