Recruitment of tyrosine phosphatase HCP by the killer cell inhibitor receptor
- PMID: 8574854
- PMCID: PMC2423819
- DOI: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80300-3
Recruitment of tyrosine phosphatase HCP by the killer cell inhibitor receptor
Abstract
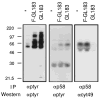
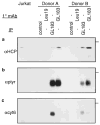
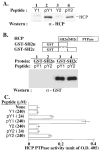
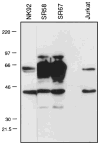
Cytolysis of target cells by natural killer (NK) cells and by some cytotoxic T cells occurs unless prevented by inhibitory receptors that recognize MHC class I on target cells. Human NK cells express a p58 inhibitory receptor specific for HLA-C. We report association of the tyrosine phosphatase HCP with the p58 receptor in NK cells. HCP association was dependent on tyrosine phosphorylation of p58. Phosphotyrosyl peptides corresponding to the p58 tail bound and activated HCP in vitro. Furthermore, introduction of an inactive mutant HCP into an NK cell line prevented the p58-mediated inhibition of target cell lysis. These data imply that the inhibitory function of p58 is dependent on its tyrosine phosphorylation and on recruitment and activation of HCP.
Figures




Comment in
-
Inhibitory receptors and their mode of action: key insights from NK cells.J Immunol. 2013 Oct 1;191(7):3489-90. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302158. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24058191 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Inhibitory receptors and their mode of action: key insights from NK cells.J Immunol. 2013 Oct 1;191(7):3489-90. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302158. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24058191 No abstract available.
-
The human natural killer cell receptor for major histocompatibility complex class I molecules. Surface modulation of p58 molecules and their linkage to CD3 zeta chain, Fc epsilon RI gamma chain and the p56lck kinase.Eur J Immunol. 1994 Oct;24(10):2527-34. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830241040. Eur J Immunol. 1994. PMID: 7523145
-
Existence of both inhibitory (p58) and activatory (p50) receptors for HLA-C molecules in human natural killer cells.J Exp Med. 1995 Sep 1;182(3):875-84. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.3.875. J Exp Med. 1995. PMID: 7650491 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of natural killer cell activation signals by killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (CD158).Immunol Rev. 2001 Jun;181:223-33. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-065x.2001.1810119.x. Immunol Rev. 2001. PMID: 11513144 Review.
-
Killer cell inhibitory receptors: diversity, specificity, and function.Immunol Rev. 1997 Feb;155:135-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1997.tb00946.x. Immunol Rev. 1997. PMID: 9059889 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of CD245 as myosin 18A, a receptor for surfactant A: A novel pathway for activating human NK lymphocytes.Oncoimmunology. 2016 Jan 13;5(5):e1127493. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2015.1127493. eCollection 2016 May. Oncoimmunology. 2016. PMID: 27467939 Free PMC article.
-
On the cell biology of pit cells, the liver-specific NK cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2000 Feb;6(1):1-11. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v6.i1.1. World J Gastroenterol. 2000. PMID: 11819514 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Dynamic variability in SHP-1 abundance determines natural killer cell responsiveness.Sci Signal. 2021 Nov 9;14(708):eabe5380. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.abe5380. Epub 2021 Nov 9. Sci Signal. 2021. PMID: 34752140 Free PMC article.
-
The mother-child union: the case of missing-self and protection of the fetus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Jun 10;94(12):5998-6000. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.12.5998. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997. PMID: 9177157 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Functional role for Syk tyrosine kinase in natural killer cell-mediated natural cytotoxicity.J Exp Med. 1997 Dec 15;186(12):1965-74. doi: 10.1084/jem.186.12.1965. J Exp Med. 1997. PMID: 9396765 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amigorena S, Bonnerot C, Drake JR, Choquet D, Hunziker W, Guillet JG, Webster P, Sautes C, Mellman I, Fridman WH. Cytoplasmic domain heterogeneity and functions of IgG Fc receptors in B lymphocytes. Science. 1992;256:1808–1812. - PubMed
-
- Beaven MA, Metzger H. Signal transduction by Fc receptors: the Fc epsilon RI case. Immunol Today. 1993;14:222–226. - PubMed
-
- Bottino C, Vitale M, Olcese L, Sivori S, Morelli L, Augugliaro R, Ciccone E, Moretta L, Moretta A. The human natural killer cell receptor for major histocompatibility complex class I molecules: surface modulation of p58 molecules and their linkage to CD3 zeta chain, FcepsilonRI gamma chain and the p56lck kinase. Eur J Immunol. 1994;24:2527–2534. - PubMed
-
- Cambier JC. New nomenclature for the Reth motif (or ARH1/TAM/ARAM/YXXL) Immunol Today. 1995;16:110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

