Developmental control of a G1-S transcriptional program in Drosophila
- PMID: 8050359
- PMCID: PMC2753441
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.120.6.1503
Developmental control of a G1-S transcriptional program in Drosophila
Abstract
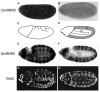
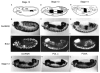
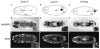
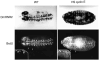
We have defined a coordinate program of transcription of S-phase genes (DNA polymerase alpha, PCNA and the two ribonucleotide reductase subunits) that can be induced by the G1 cyclin, cyclin E. In Drosophila embryos, this program drives an intricate spatial and temporal pattern of gene expression that perfectly parallels the embryonic program of S-phase control. This dynamic pattern of expression is not disrupted by a mutation, string, that blocks the cell cycle. Thus, the transcriptional program is not a secondary consequence of cell cycle progression. We suggest that developmental signals control this transcriptional program and that its activation either directly or indirectly drives transition from G1 to S phase in the stereotyped embryonic pattern.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mutations in Drosophila DP and E2F distinguish G1-S progression from an associated transcriptional program.Genes Dev. 1997 Aug 1;11(15):1999-2011. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.15.1999. Genes Dev. 1997. PMID: 9271122 Free PMC article.
-
Ectopic cyclin E expression induces premature entry into S phase and disrupts pattern formation in the Drosophila eye imaginal disc.Development. 1995 Oct;121(10):3371-9. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.10.3371. Development. 1995. PMID: 7588070
-
A Drosophila G1-specific cyclin E homolog exhibits different modes of expression during embryogenesis.Development. 1993 Nov;119(3):673-90. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.3.673. Development. 1993. PMID: 8187637
-
Cyclin A2 transcriptional regulation: modulation of cell cycle control at the G1/S transition by peripheral cues.Biochem Pharmacol. 2000 Oct 15;60(8):1179-84. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(00)00384-1. Biochem Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 11007956 Review.
-
Control of cell cycle transcription during G1 and S phases.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Aug;14(8):518-28. doi: 10.1038/nrm3629. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23877564 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A genetic screen for modifiers of E2F in Drosophila melanogaster.Genetics. 1999 Sep;153(1):275-87. doi: 10.1093/genetics/153.1.275. Genetics. 1999. PMID: 10471712 Free PMC article.
-
A role for Ebi in neuronal cell cycle control.EMBO J. 2000 Oct 16;19(20):5376-86. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.20.5376. EMBO J. 2000. PMID: 11032805 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental control of histone mRNA and dSLBP synthesis during Drosophila embryogenesis and the role of dSLBP in histone mRNA 3' end processing in vivo.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Apr;22(7):2267-82. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.7.2267-2282.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11884612 Free PMC article.
-
Control of Drosophila endocycles by E2F and CRL4(CDT2).Nature. 2011 Oct 30;480(7375):123-7. doi: 10.1038/nature10579. Nature. 2011. PMID: 22037307 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical Embryology Redux: Metabolic Control of Development.Trends Genet. 2020 Aug;36(8):577-586. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2020.05.007. Epub 2020 Jun 9. Trends Genet. 2020. PMID: 32532533 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Andrews BJ, Herskowitz I. Identification of a DNA binding factor involved in cell-cycle control of the yeast HO gene. Cell. 1989;57:21–29. - PubMed
-
- Andrews BJ, Herskowitz I. Regulation of cell cycle-dependent gene expression in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:14057–14060. - PubMed
-
- Baldin V, Lukas J, Marcote MJ, Pagano M, Draetta G. Cyclin D1 is a nuclear protein required for cell cycle progression in G1. Genes Dev. 1993;7:812–821. - PubMed
-
- Bjorklund S, Skog S, Tribukait B, Thelander L. S-phase-specific expression of mammalian ribonucleotide reductase R1 and R2 subunit mRNAs. Biochemistry. 1990;29:5452–5458. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

