Optimizing design of genomics studies for clonal evolution analysis
- PMID: 39678206
- PMCID: PMC11645549
- DOI: 10.1093/bioadv/vbae193
Optimizing design of genomics studies for clonal evolution analysis
Abstract
Motivation: Genomic biotechnology has rapidly advanced, allowing for the inference and modification of genetic and epigenetic information at the single-cell level. While these tools hold enormous potential for basic and clinical research, they also raise difficult issues of how to design studies to deploy them most effectively. In designing a genomic study, a modern researcher might combine many sequencing modalities and sampling protocols, each with different utility, costs, and other tradeoffs. This is especially relevant for studies of somatic variation, which may involve highly heterogeneous cell populations whose differences can be probed via an extensive set of biotechnological tools. Efficiently deploying genomic technologies in this space will require principled ways to create study designs that recover desired genomic information while minimizing various measures of cost.
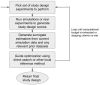
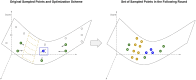
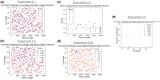
Results: The central problem this paper attempts to address is how one might create an optimal study design for a genomic analysis, with particular focus on studies involving somatic variation that occur most often with application to cancer genomics. We pose the study design problem as a stochastic constrained nonlinear optimization problem. We introduce a Bayesian optimization framework that iteratively optimizes for an objective function using surrogate modeling combined with pattern and gradient search. We demonstrate our procedure on several test cases to derive resource and study design allocations optimized for various goals and criteria, demonstrating its ability to optimize study designs efficiently across diverse scenarios.
Availability and implementation: https://github.com/CMUSchwartzLab/StudyDesignOptimization.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Update of
-
Optimizing Design of Genomics Studies for Clonal Evolution Analysis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 15:2024.03.14.585055. doi: 10.1101/2024.03.14.585055. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Bioinform Adv. 2024 Dec 02;4(1):vbae193. doi: 10.1093/bioadv/vbae193 PMID: 38559253 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Optimizing Design of Genomics Studies for Clonal Evolution Analysis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 15:2024.03.14.585055. doi: 10.1101/2024.03.14.585055. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Bioinform Adv. 2024 Dec 02;4(1):vbae193. doi: 10.1093/bioadv/vbae193 PMID: 38559253 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
How to create accessible research summaries for the developmental language disorder community.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2025 Jan-Feb;60(1):e13142. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.13142. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2025. PMID: 39625399
-
Using Experience Sampling Methodology to Capture Disclosure Opportunities for Autistic Adults.Autism Adulthood. 2023 Dec 1;5(4):389-400. doi: 10.1089/aut.2022.0090. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Autism Adulthood. 2023. PMID: 38116059 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the scientific knowledge and approaches to defining and measuring hate crime, hate speech, and hate incidents: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2024 Apr 28;20(2):e1397. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1397. eCollection 2024 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38686101 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abramson MA. Pattern Search Algorithms for Mixed Variable General Constrained Optimization Problems. Houston, Texas, United States: Rice University, 2003.
-
- Audet C, Dennis JE Jr. Pattern search algorithms for mixed variable programming. SIAM J Optim 2001;11:573–94.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

