Roscovitine, a CDK Inhibitor, Reduced Neuronal Toxicity of mHTT by Targeting HTT Phosphorylation at S1181 and S1201 In Vitro
- PMID: 39596381
- PMCID: PMC11594617
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252212315
Roscovitine, a CDK Inhibitor, Reduced Neuronal Toxicity of mHTT by Targeting HTT Phosphorylation at S1181 and S1201 In Vitro
Abstract
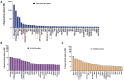
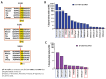
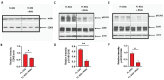
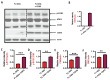
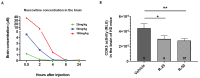
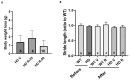
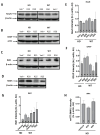
Huntington's disease (HD) is an autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disease caused by a single mutation in the huntingtin gene (HTT). Normal HTT has a CAG trinucleotide repeat at its N-terminal within the range of 36. However, once the CAG repeats exceed 37, the mutant gene (mHTT) will encode mutant HTT protein (mHTT), which results in neurodegeneration in the brain, specifically in the striatum and other brain regions. Since the mutation was discovered, there have been many research efforts to understand the mechanism and develop therapeutic strategies to treat HD. HTT is a large protein with many post-translational modification sites (PTMs) and can be modified by phosphorylation, acetylation, methylation, sumoylation, etc. Some modifications reduced mHTT toxicity both in cell and animal models of HD. We aimed to find the known kinase inhibitors that can modulate the toxicity of mHTT. We performed an in vitro kinase assay using HTT peptides, which bear different PTM sites identified by us previously. A total of 368 kinases were screened. Among those kinases, cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) affected the serine phosphorylation on the peptides that contain S1181 and S1201 of HTT. We explored the effect of CDK1 and CDK5 on the phosphorylation of these PTMs of HTT and found that CDK5 modified these two serine sites, while CDK5 knockdown reduced the phosphorylation of S1181 and S1201. Modifying these two serine sites altered the neuronal toxicity induced by mHTT. Roscovitine, a CDK inhibitor, reduced the p-S1181 and p-S1201 and had a protective effect against mHTT toxicity. We further investigated the feasibility of the use of roscovitine in HD mice. We confirmed that roscovitine penetrated the mouse brain by IP injection and inhibited CDK5 activity in the brains of HD mice. It is promising to move this study to in vivo for pre-clinical HD treatment.
Keywords: CDK5; Huntington’s disease; post-translational modification (PTM); roscovitine; toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
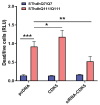
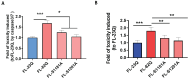
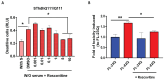
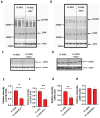
Similar articles
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Ceftazidime with avibactam for treating severe aerobic Gram-negative bacterial infections: technology evaluation to inform a novel subscription-style payment model.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(73):1-230. doi: 10.3310/YAPL9347. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39487661 Free PMC article.
-
Using Experience Sampling Methodology to Capture Disclosure Opportunities for Autistic Adults.Autism Adulthood. 2023 Dec 1;5(4):389-400. doi: 10.1089/aut.2022.0090. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Autism Adulthood. 2023. PMID: 38116059 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidants for female subfertility.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 28;7(7):CD007807. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007807.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Aug 27;8:CD007807. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007807.pub4 PMID: 28752910 Free PMC article. Updated. Review.
References
-
- MacDonald M.E., Ambrose C.M., Duyao M.P., Myers R.H., Lin C., Srinidhi L., Barnes G., Taylor S.A., James M., Groot N., et al. A novel gene containing a trinucleotide repeat that is expanded and unstable on Huntington’s disease chromosomes. The Huntington’s Disease Collaborative Research Group. Cell. 1993;72:971–983. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90585-E. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

