Safety and pharmacokinetics of vepdegestrant in Japanese patients with ER+ advanced breast cancer: a phase 1 study
- PMID: 39565495
- PMCID: PMC11700046
- DOI: 10.1007/s10147-024-02648-3
Safety and pharmacokinetics of vepdegestrant in Japanese patients with ER+ advanced breast cancer: a phase 1 study
Abstract
Background: Vepdegestrant (ARV-471) is an oral PROteolysis TArgeting Chimera (PROTAC) estrogen receptor (ER) degrader.
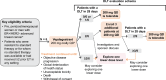
Methods: This phase 1 study (NCT05463952) investigated safety, pharmacokinetics, and antitumor activity of vepdegestrant in Japanese patients with ER-positive (ER+)/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative (HER2-) advanced breast cancer at the 200-mg once daily (QD) recommended phase 3 dose. Eligible patients had ER+/HER2- advanced breast cancer resistant to standard therapy, with no standard therapy available, or had received two or more prior endocrine therapies in any setting. The primary endpoint was dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs) in cycle 1; secondary endpoints included safety, pharmacokinetics, and antitumor activity.
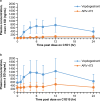
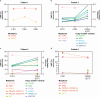
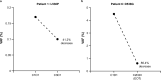
Results: Six female patients (median age, 58 [range: 47-62] years) were treated. For advanced disease, three (50.0%) patients received three or more prior regimens and five (83.3%) patients received prior cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors. At data cutoff, median treatment duration was 9.8 (range: 6-28) weeks; two patients remained on treatment. No DLTs were observed. Four (66.7%) patients experienced adverse events; none led to dose reduction or discontinuation. Four (66.7%) patients had treatment-related adverse events; all were grade 1 except anemia (grade 2). Geometric mean maximum plasma concentration and 24-h area under the plasma concentration-time curve of vepdegestrant were 630.9 ng/mL and 10,400 ng∙hr/mL after a single dose and 1056 ng/mL and 18,310 ng∙hr/mL after multiple doses. Two (33.3%) patients demonstrated stable disease at week 24.
Conclusion: Vepdegestrant 200 mg QD was well tolerated in Japanese patients with ER+/HER2- advanced breast cancer with no notable differences in pharmacokinetics from Western patients.
Clinical trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT05463952 (date of registration: July 19, 2022).
Keywords: Advanced breast cancer; Estrogen receptor–positive; Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–negative; Japanese patients; Safety; Vepdegestrant.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: H Iwata has received honoraria and research funding from Pfizer. Y Naito has received honoraria and/or other fees for conference attendance from Chugai, Daiichi Sankyo, and Eli Lilly; received research funds from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chugai, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Pfizer, Taiho, and Takeda. M Hattori has received honoraria from Daiichi Sankyo, MSD, and Eli Lilly; received research funding from Konica Minolta. A Yoshimura has nothing to disclose. K Yonemori has received honoraria from Pfizer, Eisai, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Takeda, Chugai, Fuji Film Pharma, PDR pharma, MSD, Boehringer Ingelheim, Ono, Daiichi Sankyo, Bayer, Jansen, Asteras, Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis, Sanofi, and Merk Biopharma; received research support (to institution) from MSD, Daiichi Sankyo, Merk Biopharma, AstraZeneca, Taiho, Pfizer, Novartis, Takeda, Chugai, Ono, Sanofi, Seattle Genetics, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Genmab, Boehringer Ingelheim, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Nihon Kayaku, and Haihe. M Aizawa is an employee of Pfizer R&D Japan. Y Mori is an employee of Pfizer R&D Japan and holds stock in Pfizer Inc. J Yoshimitsu is an employee of Pfizer R&D Japan. Y Umeyama is an employee of Pfizer R&D Japan and holds stock in Pfizer Inc. T Mukohara has received honoraria from Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Eisai, Pfizer, Novartis, Chugai, AstraZeneca, Kyowa Kirin, and Taiho; received research funds from AstraZeneca, Chugai, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Gilead Sciences, MSD, Novartis, Ono, Pfizer, Sanofi, and Sysmex. Role of the sponsor: The funders had a role in the design and conduct of the study; data collection, management, and analysis of the data. The drafting of the manuscript, review, and decision to submit for publication were made by all the authors. Ethical approval: Approval of the study protocol by an Institutional Reviewer Board: The protocol, ICF, Investigator Brochure, and other relevant documents were submitted to an IRB/EC by the investigator and reviewed and approved by the IRB/EC before the study was initiated. These IRBs include the following: IRB at Aichi Cancer Center Hospital, IRB at National Cancer Center Hospital East, and IRB at National Cancer Center Hospital. This study was conducted in accordance with the protocol and consensus ethical principles derived from international guidelines, including the Declaration of Helsinki Council and CIOMS International Ethical Guidelines, applicable ICH GCP Guidelines, applicable ISO 14155 guidelines, medical device guidelines, and other applicable laws and regulations, including privacy laws. Informed consent: All patients provided written informed consent prior to the study. Registry and the Registration no. of the study/trial: This study is registered on ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT05463952). Research involving human and animal rights: Not applicable.
Figures

Similar articles
-
VERITAC-2: a Phase III study of vepdegestrant, a PROTAC ER degrader, versus fulvestrant in ER+/HER2- advanced breast cancer.Future Oncol. 2024;20(32):2447-2455. doi: 10.1080/14796694.2024.2377530. Epub 2024 Jul 29. Future Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39072356 Free PMC article.
-
Oral Estrogen Receptor PROTAC Vepdegestrant (ARV-471) Is Highly Efficacious as Monotherapy and in Combination with CDK4/6 or PI3K/mTOR Pathway Inhibitors in Preclinical ER+ Breast Cancer Models.Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Aug 15;30(16):3549-3563. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-3465. Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38819400 Free PMC article.
-
Phase 1 study of oral selective estrogen receptor degrader (SERD) amcenestrant (SAR439859), in Japanese women with ER-positive and HER2-negative advanced breast cancer (AMEERA-2).Breast Cancer. 2023 May;30(3):506-517. doi: 10.1007/s12282-023-01443-8. Epub 2023 Mar 29. Breast Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36977973 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A phase I dose escalation and expansion trial of the next-generation oral SERD camizestrant in women with ER-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer: SERENA-1 monotherapy results.Ann Oncol. 2024 Aug;35(8):707-717. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2024.04.012. Epub 2024 May 8. Ann Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38729567 Clinical Trial.
-
Stability Evaluation and Pharmacokinetic Profiling of Vepdegestrant in Rodents Using Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry.Molecules. 2024 Aug 27;29(17):4048. doi: 10.3390/molecules29174048. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39274896 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL et al (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71:209–249. 10.3322/caac.21660 - PubMed
-
- Giaquinto AN, Sung H, Miller KD et al (2022) Breast cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin 72:524–541. 10.3322/caac.21754 - PubMed
-
- Huppert LA, Gumusay O, Idossa D et al (2023) Systemic therapy for hormone receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative early stage and metastatic breast cancer. CA Cancer J Clin 73:480–515. 10.3322/caac.21777 - PubMed
-
- Cancer stat facts: female breast cancer subtypes. National Cancer Institute: Surveillance, Epidemology, and End Results Program. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/breast-subtypes.html. Accessed 16 Apr 2024
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

