Efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 immune checkpoint inhibitors in the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39555073
- PMCID: PMC11563947
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1485303
Efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 immune checkpoint inhibitors in the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors combined with CTLA-4 inhibitors in the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer is controversial. This meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors combined with CTLA-4 inhibitors for advanced colorectal cancer.
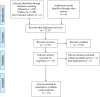
Methods: PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Library, and Web of Science databases were systematically searched for relevant studies. Outcomes including median progression-free survival (mPFS), median overall survival (mOS), overall response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) and ≥grade 3 TRAEs were extracted for further analysis. The risk of bias was assessed by subgroup analysis.
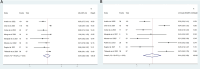
Results: 12 articles with 566 patients were identified and subjected to meta-analysis. With regard to survival analysis, the pooled mOS and mPFS were 6.66 months (95%CI 4.85-9.16) and 2.92 months (95%CI 2.23-3.83), respectively. In terms of tumor response, the pooled ORR and DCR were 21% (95%CI 6%-41%) and 49% (95%CI 27%-71%), respectively. The pooled AEs rate and ≥ grade 3 AEs rate were 94% (95%CI 86%-99%) and 44% (95%CI 30%-58%).
Conclusion: PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors combined with CTLA-4 inhibitors have shown promising clinical responses in the treatment of colorectal cancer (CRC). Although the incidence of adverse reactions is high, they are generally tolerable.
Systematic review registration: https://inplasy.com/, identifier INPLASY202480030.
Keywords: CTLA-4; PD-1; PD-L1; colorectal cancer; immune checkpoint inhibitors; immunotherapy.
Copyright © 2024 Song, Hou, Ma, Yan and Gao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparison of efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 combination therapy in first-line treatment of advanced NSCLC: an updated systematic review and network meta-analysis.Clin Transl Oncol. 2024 Oct;26(10):2488-2502. doi: 10.1007/s12094-024-03442-3. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Clin Transl Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38625495
-
Efficacy and safety of PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors in advanced colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.BMC Gastroenterol. 2024 Dec 18;24(1):461. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03554-8. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39696009 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of efficacy of the first-line treatment for advanced non-small cell lung cancer with primary MET-amplification: Retrospective evaluation of 36 cases.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Dec 25;143(Pt 2):113391. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113391. Epub 2024 Oct 19. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39427497
-
PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors for early and middle stage microsatellite high-instability and stable colorectal cancer: a review.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2024 May 29;39(1):83. doi: 10.1007/s00384-024-04654-3. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2024. PMID: 38809459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarkers to predict efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in colorectal cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Exp Med. 2024 Jul 3;24(1):143. doi: 10.1007/s10238-024-01408-x. Clin Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 38960935 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

