Cleistopholis patens root bark extract exerts cardioprotective effect against doxorubicin-induced myocardial toxicity in rats
- PMID: 39551811
- PMCID: PMC11572060
- DOI: 10.1186/s42826-024-00225-3
Cleistopholis patens root bark extract exerts cardioprotective effect against doxorubicin-induced myocardial toxicity in rats
Abstract
Background: Myocardial Infarction still persists as the most prevalent cardiovascular disease and is a top cause of morbidity and mortality in doxorubicin treated cancer patients. This study evaluated the prophylactic effect of the ethanol root bark extract of Cleistopholis patens (ERBECP) against doxorubicin-induced myocardial infarction in wistar rats. Extraction, preliminary phytochemical analysis, acute toxicity study and body weight (b.w.) of ERBECP were achieved using standard methods. Phyto-constituents in ERBECP were indentified using Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) technique. Thirty (30) male albino Wistar rats of average b.w. ranging between 100 and 130 g were divided into six groups of five rats each. Groups I, II and III served as normal, doxorubicin (DOX) and standard (Vasoprin 150 mg/kg b.w) controls respectively, while groups IV, V and VI were orally pre-treated with the extract (200, 400 and 600 mg/kgb.w) for two weeks prior to intraperitoneal induction of cardiotoxicity with DOX (20 mg/kg bw) on day 14.
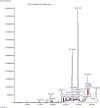
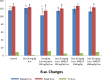
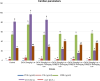
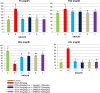
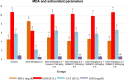
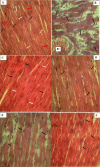
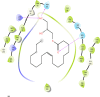
Results: Disturbances in serum cardiac function bio-markers such as; Cardiac Troponin-I (CTnI), Creatine Kinase (CK), Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH), Aspartate aminotransferase (AST), Alanine aminotransferase (ALT). Lipid profile markers such as; Total cholesterol (TC), Triacylglycerol (TAG), Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL), High Density Lipoprotein (HDL). Oxidative stress markers such as; Malondialdehyde (MDA), Superoxide Dismutase (SOD), Catalase (CAT), Glutathione (GSH) confirmed the induction of myocardial infarction. Histological assessment of heart tissues was performed to validate biochemical results. The GC-MS analysis of ERBECP identified a total of 69 compounds. Safety profile of the aqueous extract was safe for the animals up to the highest dose of 5000 mg/kg b.w. Pre-treatment of DOX group with ERBECP could significantly increase the b.w. compared to the DOX-treated group during the experimental period of 2 weeks. There were significant (p < 0.05) alterations in the levels of CTnI, CK, LDH, AST, ALT and lipid profile indices in the DOX control rats. Also, significant (p < 0.05) increase was observed in MDA and decrease in SOD, CAT and GSH in the DOX control rats. However, administration of the extract significantly (p < 0.05) normalized these alterations and reversed the architectural changes in the heart. The 69 compounds were screened against the target protein (CBR1); we identified seven hits based on the docking score and interactions with the active site residues. All the C. patens constituents had MW (g/mol) less than 500, HBA < 10 and HBD not more than 5. Apart, 9-Octadecenoic acid (Z)-, 2,3-dihydroxy propyl ester and Estra-1,3,5(10)-trien-17. beta. -ol, all the constituents had LD50 lower than 2000 mg/kg.
Conclusions: The findings reveals ERBECP demonstrated promising potential and can be exploited in the development novel cardiac therapeutic agents.
Keywords: Cleistopholis patens; Cardiotoxicity; Doxorubicin; Histopathology; Myocardial infarction; Oxidative stress.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







Similar articles
-
Cardioprotective effect of ascorbic acid on doxorubicin-induced myocardial toxicity in rats.Indian J Pharmacol. 2011 Sep;43(5):507-11. doi: 10.4103/0253-7613.84952. Indian J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 22021990 Free PMC article.
-
Genotoxicity, nitric oxide level modulation and cardio-protective potential of Kalanchoe Integra Var. Crenata (Andr.) Cuf Leaves in murine models.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Jan 30;283:114640. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114640. Epub 2021 Oct 2. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34606947
-
Cardioprotective effect of HPLC standardized ethanolic extract of Terminalia pallida fruits against isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in albino rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 May 7;141(1):33-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.01.011. Epub 2012 Feb 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22366678
-
The role of hesperidin as a cardioprotective strategy against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: The antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antiapoptotic, and cytoprotective potentials.Open Vet J. 2023 Dec;13(12):1718-1728. doi: 10.5455/OVJ.2023.v13.i12.20. Epub 2023 Dec 31. Open Vet J. 2023. PMID: 38292716 Free PMC article.
-
Cinnamomum zeylanicum Blume (Ceylon cinnamon) bark extract attenuates doxorubicin induced cardiotoxicity in Wistar rats.Saudi Pharm J. 2021 Aug;29(8):820-832. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2021.06.004. Epub 2021 Jun 20. Saudi Pharm J. 2021. PMID: 34408544 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arul A, Nayagam J, Gunasekaran S, Rangarajan S, Muthaiah S. Myocardial potency of Caesalpinia bonducella Linn. on doxorubicin induced myocardial infarction in albino rats. Clin Phytoscience. 2019;5:1–7.
-
- Ojha N, Dhamoon AS. Myocardial Infarction. StatPearls-NCBI Bookshelf, (n.d.). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537076/.
-
- Tibaut M, Mekiš D, Petrovič D. Pathophysiology of myocardial infarction and acute management strategies. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2016;14:150–8. - PubMed
-
- Khadse NA, Wankhade AM, Gaiki AG. Myocardial infraction : etiology, risk factors, pathophysiology, diagnosis and management. Am J PharmTech Res. 2020;10:1–18.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

