The potential of kaempferol in digestive system tumors: recent advances and mechanistic insights
- PMID: 39546109
- PMCID: PMC11568081
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-024-01510-2
The potential of kaempferol in digestive system tumors: recent advances and mechanistic insights
Abstract
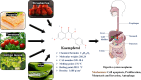
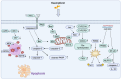
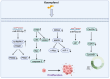
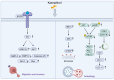
Digestive system neoplasms are a heterogeneous group of cancers characterized by diverse symptoms, complex diagnosis, and treatment. Prognosis is poor and influenced by multiple factors, making early detection and comprehensive treatment crucial for patient survival. Kaempferol, a flavonoid compound, has attracted attention due to its anti-tumor biological activity, holding promise as a potential drug for treating digestive system neoplasms. Derived from various plants such as cabbage, propolis, and grapefruit, this compound's anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and other pharmacological effects have been confirmed. Research has found that kaempferol inhibits the occurrence and development of digestive system neoplasms by inducing apoptosis in cancer cells, inhibiting tumor cell proliferation, suppressing tumor metastasis and invasion, and enhancing the effects of other cancer treatment methods. This paper summarizes the role and mechanisms of kaempferol in the study of digestive system neoplasms, providing valuable insights for both scientists and clinical physicians engaged in this field. By detailing the various pathways through which kaempferol exerts its anticancer effects, the paper not only highlights its potential as a therapeutic agent but also opens avenues for further research into its applications.
Keywords: Digestive system neoplasms; Flavonoids; Kaempferol; Mechanism; Pathway.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of kaempferol in gynaecological malignancies: progress and perspectives.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Dec 4;14:1310416. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1310416. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38143502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kaempferol from Alpinia officinarum hance induces G2/M cell cycle arrest in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by regulating the ATM/CHEK2/KNL1 pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Oct 28;333:118430. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118430. Epub 2024 Jun 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38857680
-
Kaempferol Inhibits Cervical Cancer Cells by Inducing Apoptosis and Autophagy via Inactivation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway.Anticancer Res. 2024 Jul;44(7):2961-2972. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.17108. Anticancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38925830
-
The Anticancer Effects and Therapeutic Potential of Kaempferol in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Nutrients. 2024 Jul 23;16(15):2392. doi: 10.3390/nu16152392. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39125273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kaempferol, a potential cytostatic and cure for inflammatory disorders.Eur J Med Chem. 2014 Oct 30;86:103-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.08.011. Epub 2014 Aug 5. Eur J Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 25147152 Review.
References
-
- Hojman P, et al. Molecular mechanisms linking exercise to cancer prevention and treatment. Cell Metab. 2018;27(1):10–21. - PubMed
-
- Habal N, Sims C, Bilchik AJ. Gastrointestinal carcinoid tumors and second primary malignancies. J Surg Oncol. 2000;75(4):310–6. - PubMed
-
- Sung H, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, et al. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72(1):7–33. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
