Association between life's essential 8 and cognitive impairment in older patients: results from NHANES 2011-2014
- PMID: 39543520
- PMCID: PMC11566281
- DOI: 10.1186/s12877-024-05547-4
Association between life's essential 8 and cognitive impairment in older patients: results from NHANES 2011-2014
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to examine the association between the American Heart Association's (AHA) newly revised Life's Essential 8 (LE8) algorithm, designed for assessing cardiovascular health (CVH), and cognitive impairment among older adults in the United States.
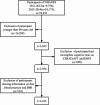
Methods: This study employed a cross-sectional design, utilizing data from the 2011-2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey to explore the relationship between CVH and cognitive impairment in older adults. CVH scores are assessed based on the AHA definition of the LE8, categorized into three tiers: low (0-49), medium (50-79), and high (80-100). Cognitive impairment is evaluated using three distinct scoring systems: the Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer's Disease (CERAD), the Animal Fluency Test (AFT), and the Digit Symbol Substitution Test (DSST). The lowest quartile as the cut-off point; below or equal to the lower quartile was considered as low cognitive population, and above the lower quartile was normal population. To analyze the association, multivariable logistic regression and restricted cubic spline (RCS) models were employed.
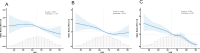
Results: A significant negative correlation exists between the LE8 and cognitive impairment. After adjusting for multiple variables, the odds ratios (OR) for cognitive impairment, as measured by the CERAD, AFT, and DSST, were compared between patients with high and low CVH. The results indicated OR values of 0.60 (95% CI: 0.36-0.98), 0.72 (95% CI: 0.52-0.97), and 0.29 (95% CI: 0.16-0.53) for the CERAD, AFT, and DSST, respectively. Additionally, the RCS curve demonstrated a significant linear relationship between lifestyle factors encapsulated by the LE8 and cognitive impairment.
Conclusions: The findings indicate higher adherence to LE8 was associated with lower odds of cognitive impairment. Furthermore, maintaining optimal CVH is crucial in preventing cognitive impairment.
Keywords: Cardiovascular health; Cognitive impairment; Life’s essential 8; NHANES.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of Cardiovascular Health with Cognitive Function in US Older Adults: A Population-Based Cross-Sectional Study.Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2024;53(1):1-11. doi: 10.1159/000534923. Epub 2023 Nov 17. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2024. PMID: 37980885
-
Association between Life's Essential 8 and cognitive function among older adults in the United States.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 26;14(1):19773. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70112-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39187530 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the associations between Life's Essential 8 and Life's Simple 7 with depression, as well as the mediating role of oxidative stress factors and inflammation: NHANES 2005-2018.J Affect Disord. 2024 Apr 15;351:31-39. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2024.01.200. Epub 2024 Jan 26. J Affect Disord. 2024. PMID: 38280569
-
Association between Life's Essential 8 and cognitive function: insights from NHANES 2011-2014.Front Aging Neurosci. 2024 Apr 4;16:1386498. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1386498. eCollection 2024. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38650867 Free PMC article.
-
Dose-response associations of the American Heart Association's new "Life's essential 8" metrics with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in a nationally representative sample from the United States.Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2024 Jul-Aug;85:31-37. doi: 10.1016/j.pcad.2024.06.001. Epub 2024 Jun 24. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2024. PMID: 38925257 Review.
References
-
- Dichgans M, Leys D. Vascular Cognitive Impairment. Circulation research. 2017/2/3/;120(3):573 – 91. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical