Conducting observational analyses with the target trial emulation approach: a methodological systematic review
- PMID: 39532374
- PMCID: PMC11574403
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-086595
Conducting observational analyses with the target trial emulation approach: a methodological systematic review
Abstract
Objectives: Target trial emulation is an approach that is increasingly used to improve transparency in observational studies and help mitigate biases. For studies declaring that they emulated a target trial, we aimed to evaluate the specification of the target trial, examine its consistency with the observational emulation and assess the risk of bias in the observational analysis.
Design: Methodological systematic review reported in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses statement.
Data sources: The database MEDLINE (Medical Literature Analysis and Retrieval System Online) was interrogated for all studies published from 1 January 2021 to 3 July 2022. We performed an additional manual search of 20 general medical and specialised journals that spanned the same period.
Eligibility criteria: All studies that declared emulating a hypothetical or real randomised trial were eligible.
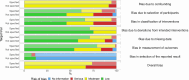
Data extraction and synthesis: Two independent reviewers performed the whole systematic review process (screening and selection of studies, data extraction and risk of bias assessment). The main outcomes were the definition of the key protocol components of the target trial and its emulation, consistency between the target trial and its emulation and risk of bias according to the ROBINS-I (Risk Of Bias In Non-randomised Studies - of Interventions) tool.
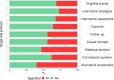
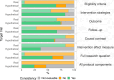
Results: Among the selected sample of 100 studies, 24 (24%) did not specify the target trial. Only 40 studies (40%) provided detailed information on all components of the target trial protocol. Eligibility criteria, intervention strategies and outcomes were consistent between the target trial and its emulation in 35 studies (46% of those specifying the target trial). Overall, 28 studies (28%) exhibited serious risk of bias and 41 (41%) had misalignments in the timing of eligibility assessment, treatment assignment and the start of follow-up (time-zero). As compared with studies that did not specify the target trial, those that did specify the trial less frequently seemed to have both time-zero issues (39% vs 52%) and serious risk of bias (26% vs 33%).
Conclusions: One-quarter of studies declaring that they emulated a target trial did not specify the trial. Target trials and their emulations were particularly inconsistent for studies emulating a real randomised trial. Risk of methodological issues seemed lower in observational analyses that specified versus did not specify the target trial.
Keywords: EPIDEMIOLOGY; Observational Study; STATISTICS & RESEARCH METHODS.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at www.icmje.org/disclosure-of-interest/ and declare that they have no competing interest related to the study. GLM declares consulting fees from Synapse Medicine, unrelated to the study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Implementation of the trial emulation approach in medical research: a scoping review.BMC Med Res Methodol. 2023 Aug 16;23(1):186. doi: 10.1186/s12874-023-02000-9. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2023. PMID: 37587484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
Reporting of Observational Studies Explicitly Aiming to Emulate Randomized Trials: A Systematic Review.JAMA Netw Open. 2023 Sep 5;6(9):e2336023. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.36023. JAMA Netw Open. 2023. PMID: 37755828 Free PMC article.
-
Healthcare outcomes assessed with observational study designs compared with those assessed in randomized trials.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Apr 29;2014(4):MR000034. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000034.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Jan 4;1:MR000034. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000034.pub3 PMID: 24782322 Free PMC article. Updated. Review.
References
-
- Hernán MA, Robins JM. Causal Inference: What If. Boca Raton: Chapman&Hall/CRC; 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
