Bioinformatics Combined With Experimental Modeling to Study the Molecular Mechanism of Xuefu Zhuyu Decoction to Improve Erectile Dysfunction Associated With Asthma in Rats
- PMID: 39520273
- PMCID: PMC11550509
- DOI: 10.1177/15579883241293936
Bioinformatics Combined With Experimental Modeling to Study the Molecular Mechanism of Xuefu Zhuyu Decoction to Improve Erectile Dysfunction Associated With Asthma in Rats
Abstract
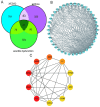
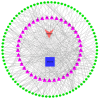
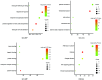
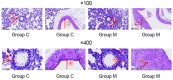
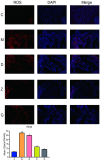
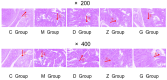
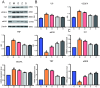
Asthma is associated with chronic systemic inflammation, and inflammatory factors can damage vascular endothelial cells, thus impairing erectile function (ED). Xuefu Zhuyu decoction (XFZYD) can inhibit inflammation and promote angiogenesis, which in turn improves asthma as well as ED, but its exact mechanism of action is not yet clear. This study investigates the mechanism underlying the beneficial effect of XFZYD on asthma-associated ED. High-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS) was used to analyze the constituents of XFZYD, and network pharmacology analysis was used to predict the target genes of XFZYD. Sprague-Dawley rats in the asthma model with erectile dysfunction were divided into the model, XFZYD low-, medium-, and high-dose group (3.09, 6.17, and 12.34 g/kg), with drug intervention for 8 weeks. We assessed the interleukin 6 (IL-6), vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA), and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) protein levels in the penile tissue. We discovered that after treatment with XFZYD (3.09, 6.17, and 12.34 g/kg), the number of erections significantly increased (1.17 ± 0.41, 1.50 ± 0.55, and 1.67 ± 0.52), the density of endothelial cells in the corpus cavernosum of the penis increased, the expression level of IL-6 was reduced (7.5%, 21.2%, and 24.4%), the expression level of VEGFA was reduced (7.8%, 25%, and 28.4%), and the expression level of TNF was reduced (13.5%, 30.6%, and 32.4%). The in vivo experiments indicate that XFZYD may improve ED in asthma model rats by inhibiting inflammation and reducing vascular permeability. This study provides new insights into the mechanism of action of XFZYD in the treatment of asthma leading to ED.
Keywords: classical formula; erectile dysfunction; network pharmacology; target.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systematic analysis of tRNA-derived small RNAs reveals therapeutic targets of Xuefu Zhuyu decoction in the cortexes of experimental traumatic brain injury.Phytomedicine. 2022 Jul 20;102:154168. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154168. Epub 2022 May 14. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35623157
-
TMT-based proteomics analysis reveals the protective effects of Xuefu Zhuyu decoction in a rat model of traumatic brain injury.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Aug 10;258:112826. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112826. Epub 2020 Apr 13. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32298754
-
Xuefu Zhuyu decoction promotes synaptic plasticity by targeting miR-191a-5p/BDNF-TrkB axis in severe traumatic brain injury.Phytomedicine. 2024 Jul;129:155566. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155566. Epub 2024 Mar 23. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38565001
-
Xuefu Zhuyu decoction improves asthma-induced asthenozoospermia based on network pharmacology and in vivo experiment.Andrologia. 2021 Nov;53(10):e14198. doi: 10.1111/and.14198. Epub 2021 Aug 10. Andrologia. 2021. PMID: 34375006
-
A Chinese classical prescription Xuefu Zhuyu decoction in the treatment of coronary heart disease: An overview.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 4;10(7):e28919. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28919. eCollection 2024 Apr 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38617912 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Araña Rosaínz Mde J., Ojeda M. O., Acosta J. R., Elías-Calles L. C., González N. O., Herrera O. T., García Álvarez C. T., Rodríguez E. M., Báez M. E., Seijas E. Á., Valdés R. F. (2011). Imbalanced low-grade inflammation and endothelial activation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and erectile dysfunction. The Journal of Sexual Medicine, 8(7), 2017–2030. 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2011.02277.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Broide D., Schwarze J., Tighe H., Gifford T., Nguyen M. D., Malek S., Van Uden J., Martin-Orozco E., Gelfand E. W., Raz E. (1998). Immunostimulatory DNA sequences inhibit IL-5, eosinophilic inflammation, and airway hyperresponsiveness in mice. Journal of Immunology, 161(12), 7054–7062. - PubMed
-
- Burnett A. L., Nehra A., Breau R. H., Culkin D. J., Faraday M. M., Hakim L. S., Heidelbaugh J., Khera M., McVary K. T., Miner M. M., Nelson C. J., Sadeghi-Nejad H., Seftel A. D., Shindel A. W. (2018). Erectile dysfunction: AUA guideline. The Journal of Urology, 200(3), 633–641. 10.1016/j.juro.2018.05.004 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

