Psoriasis and Seasonality: Exploring the Genetic and Epigenetic Interactions
- PMID: 39519223
- PMCID: PMC11547062
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252111670
Psoriasis and Seasonality: Exploring the Genetic and Epigenetic Interactions
Abstract
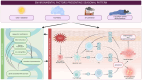
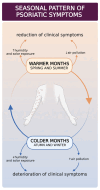
Psoriasis is a multifactorial, chronic, and inflammatory disease that severely impacts patients' quality of life. The disease is caused by genetic irregularities affected by epigenetic and environmental factors. Some of these factors may include seasonal changes, such as solar radiation, air pollution, and humidity, and changes in circadian rhythm, especially in the temporal and polar zones. Thus, some psoriasis patients report seasonal variability of symptoms. Through a comprehensive review, we aim to delve deeper into the intricate interplay between seasonality, environmental factors, and the genetic and epigenetic landscape of psoriasis. By elucidating these complex relationships, we strive to provide insights that may inform targeted interventions and personalized management strategies for individuals living with psoriasis.
Keywords: air pollution; circadian rhythm; environmental factors; epigenetics; genetics; geoepidemiology; humidity; psoriasis; seasonality; solar radiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epigenetics and seasonal timing in animals: a concise review.J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2024 Jul;210(4):565-574. doi: 10.1007/s00359-023-01673-3. Epub 2023 Sep 11. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2024. PMID: 37695537 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic and epigenetic basis of psoriasis pathogenesis.Mol Immunol. 2015 Apr;64(2):313-23. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2014.12.014. Epub 2015 Jan 13. Mol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25594889 Review.
-
Epigenetics of Psoriasis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1253:209-221. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-3449-2_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32445097 Review.
-
Epigenetics of psoriatic disease: A systematic review and critical appraisal.J Autoimmun. 2017 Mar;78:29-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2016.12.002. Epub 2016 Dec 10. J Autoimmun. 2017. PMID: 27965059 Review.
-
Genetic and Epigenetic Mechanisms of Psoriasis.Genes (Basel). 2023 Aug 13;14(8):1619. doi: 10.3390/genes14081619. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37628670 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Parisi R., Symmons D.P., Griffiths C.E., Ashcroft D.M., Identification and Management of Psoriasis and Associated ComorbidiTy (IMPACT) project team Global epidemiology of psoriasis: A systematic review of incidence and prevalence. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013;133:377–385. doi: 10.1038/jid.2012.339. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Villani A.P., Rouzaud M., Sevrain M., Barnetche T., Paul C., Richard M.A., Beylot-Barry M., Misery L., Joly P., Le Maitre M., et al. Prevalence of undiagnosed psoriatic arthritis among psoriasis patients: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015;73:242–248. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2015.05.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alinaghi F., Calov M., Kristensen L.E., Gladman D.D., Coates L.C., Jullien D., Gottlieb A.B., Gisondi P., Wu J.J., Thyssen J.P., et al. Prevalence of psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational and clinical studies. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019;80:251–265.e19. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2018.06.027. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

